Cat 6 vs Cat 6a vs Cat 7
The Key Things You Need to Know
Cat 6 vs Cat 6a vs Cat 7: Unless you are a cabling technician, you may find all of these terms cabling rather confusing. Simply put, Cat 6, Cat 6a, Cat 7, and Cat 8 all refer to different categories of network cabling. Click on each section to learn more:
1. An Overview
Cat 6 vs Cat 6a vs Cat 7 vs Cat 8
These terms may sound confusing if you’ve never heard them before. In this post we’ll help to break down the intimidating jargon for you and explain in layman’s terms what each type means and what its capabilities are.
Even though many consumer electronics are moving towards wireless technology, many local area networks (LANs) still need to use physical cabling for heavy data transmitting. As mentioned above, Cat 6, Cat 6a, Cat 7, and Cat 8 all refer to different categories of network cabling.
The following chart will give you a quick overview of the differences, but to better understand what these categories mean, read on to learn more about the basics of network cabling.
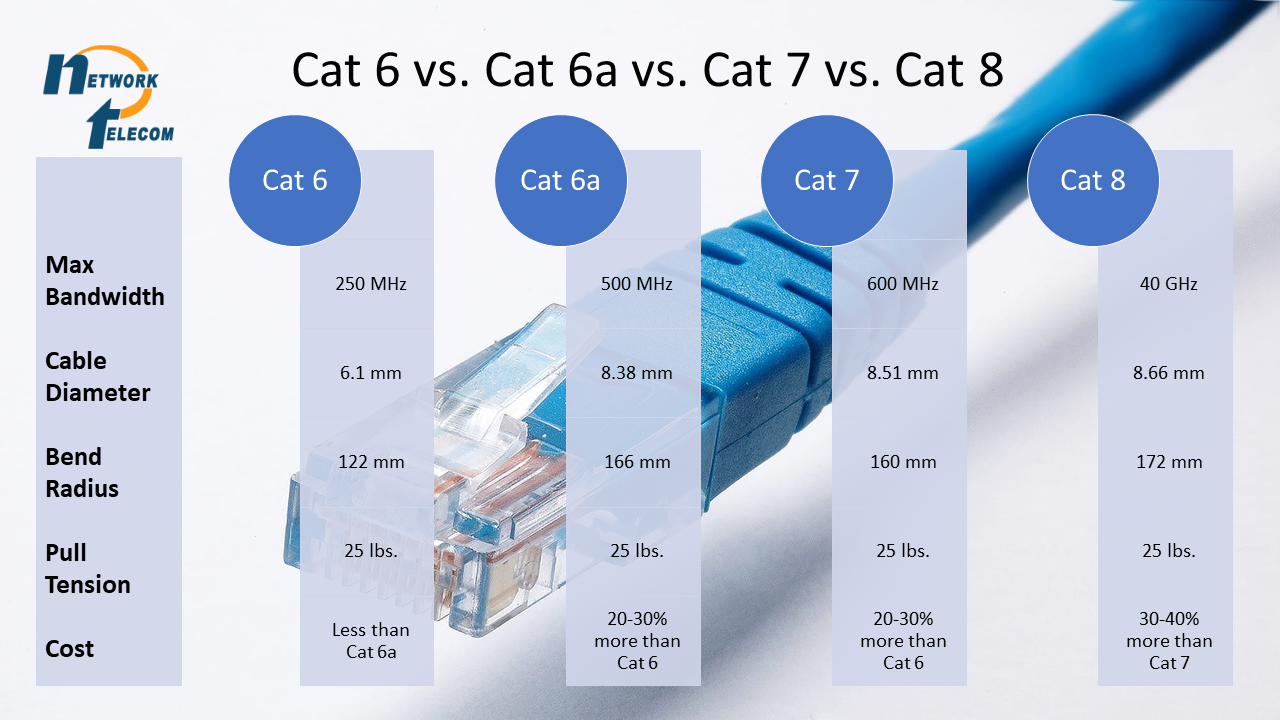
Cat 6 vs Cat 6a vs Cat 7 vs Cat 8: Learn About The Differences
2. What Is an Ethernet Cable
Ethernet cables are used to connect modems, routers, and computers together on a network. An Ethernet cable is a standard cable that was developed in the 1980s. They are thick, flexible cables that are made up of two or more wires which run side by side and are twisted, braided or bonded together.
Each end of the cable can be attached to a different device on your network. On the outside, all Ethernet cables look pretty much the same, however different categories of cables have different capabilities.

3. Types of Ethernet Cables
There are two main types of Ethernet cables: UTP (unshielded twisted pair) and STP (Shielded twisted pair).
Unshielded Twisted Pairs (UTP): Unshielded cabling does not have foil or braided shielding which makes their signal quality not as good as a shielded type and they are more susceptible to crosstalk. They are however cheaper and more flexible than the shielded cables.
Shielded Twisted Pairs (STP): Shielded cables have a braided shielding which is usually made from copper or another conductive polymer substance which helps to protect them. This protection reduces noise and crosstalk thus giving them a better connection quality.

4. What Do the Different Ethernet Cable Speeds Mean?
When looking at the speed of the various Ethernet cables it can be a bit confusing as to what they actually mean and to visualize how fast or slow each one is. To give you a clearer picture of how fast these cable speeds are, consider the following:
Imagine you were trying to download some movies. Each movie was 4.5 GB in size. If the Ethernet cable you are using has a speed of 10 Mbps then that means you would be able to download one 4.5 GB movie in one hour.
The following chart will give you a better idea of how fast each cable speed will be by showing you how many movies could be downloaded in one hour.
Ethernet Cable Speed |
# of Movies (4.5GB)
|
|---|---|
| 10 Mbps = 1.2 MB/second | 1 |
| 100 Mbps = 12 MB/second | 10 |
| 1.0 Gbps = 125 MB/second | 100 |
| 10 Gbps = 1.25 Gbps 1000 | 1000 |
5. Cat 6 vs Cat 6a vs Cat 7 vs Cat 8:
The Specifics of Each Type
What is Cat 6 (Category 6)
CAT 6 is a type of Ethernet cabling that is used for home and business networks. It is the sixth generation of twisted pair Ethernet cabling as defined by the Electronic Industries Association and Telecommunications Industry Association. CAT 6 cables are backward compatible with CAT 5 and CAT 5e, two of the previous generations of Ethernet cabling.
How Fast is Cat 6?
CAT 6 cables support Gigabit Ethernet data rates of 1 gigabit per second. This means that the theoretical maximum data rate that they can achieve is 1 gigabit per second. In reality, the speeds that you will get will be less than that due to collisions or other transient failures.
Under normal conditions though, you could get data transfer for brief periods of time of up to 900 Mbps. CAT 6 can also accommodate 10 Gigabit Ethernet connections over a limited distance. This means that up to 164 feet, a single cable could allow a 10 Gigabit Ethernet connection.

What Connectors Do CAT 6 Cables Use?
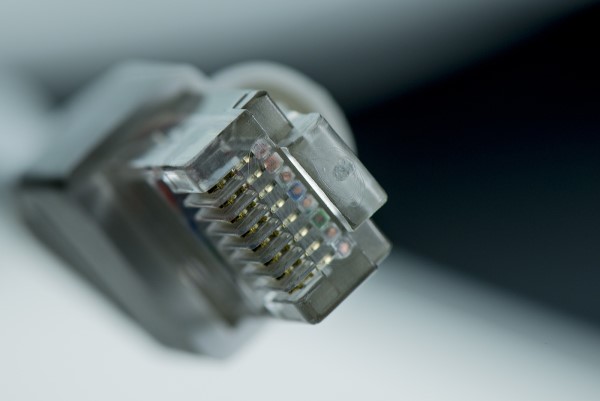
CAT 6 uses the same Registered Jack 45 (RJ-45) standard connectors that the previous generations of Ethernet cables used. RJ45 plugs have eight pins into which the wire strands of the cable interface electrically.
The individual wires of the cable are inserted about 1 mm apart using a special cable crimping tool.
The term “plug” refers to the cable or “male” end of the connection and the term “jack” refers to the “female” end or port where the connector is inserted.

What Is the Difference Between CAT 6 and CAT 6A?
The “A” added onto the CAT 6 cable means that this type of CAT 6 has been augmented.
The CAT 6A is an improvement on the CAT 6 in that it is able to accommodate 10 Gigabit Ethernet data rates up to 328 feet on a single cable.
This means that it is twice as fast as the CAT 6. They are thicker than the CAT 6 cable but they still use the same RJ-45 connectors. The faster speed of the CAT 6A does come at a higher price tag though.
CAT 6a cables have also been shielded which means that they have a thicker covering which helps to eliminate crosstalk completely.

Is There a Cat 6e Ethernet Cable?
There is some confusion surrounding the term Cat 6e, but Cat 6e is not an actual standard. When Cat 6 cables were first coming out, some manufacturers started to offer cables labelled as “Category 6e” following the pattern established by Cat 5 and Cat 5e cables.
They were trying to show that their cable was an upgrade from the Cat 6 ones just like the Cat 5e was an upgrade from the Cat 5. This was not the case though since no legitimate Category 6e standard exists and Cat 6e is not recognized by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA).
The TIA is accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) to develop standards for the telecommunications industry.

What Is Cat 7?
CAT 7 Ethernet cables support higher bandwidths and much faster transmission speeds than Cat 6 cables. As a result they are much more expensive than their Cat 6 counterparts, however, if you are looking for better performance, they are worth the extra cost. Cat 7 cables can reach up to 100 Gbps at a range of 15 meters.
This makes them a great choice for connecting modems and routers right to your devices. Like Cat 6a cables, they also come shielded to completely eliminate noise and improves your connection quality. Cat 7 cables do not use the RJ-45 connectors; they have a modified GigaGate 45 connector.
What is Cat 8?
Cat 8 ethernet cables can give you the highest data transfer rate and bandwidth frequency of any RJ45 network cables. It is the latest generation of ethernet cables.
Speed and Bandwidth:
Cat 8 boasts the highest data transfer rates and bandwidth frequencies of any RJ45 cable. We’re talking a whopping 40 Gbps (Gigabits per second) and a frequency of up to 2000 MHz.
This translates to incredibly fast data transmission, ideal for demanding applications like high-resolution video streaming, data centers, and future-proofing your network for even more advanced technologies.
Shielding:
Cat 8 cables take shielding to a whole new level. They utilize a combination of shielding methods like individual foil shielding for each twisted pair and an overall braided shield. This robust shielding significantly reduces crosstalk and electromagnetic interference (EMI) that can disrupt data signals, especially over longer distances.
Construction:
Cat 8 cables are typically made from thicker gauge wires (around 26AWG) compared to previous Cat ratings. This thicker gauge allows for better signal quality over longer cable lengths.
Cost:
Cat 8 cables are currently more expensive than previous Cat ratings due to their advanced construction and features.
Compatibility:
While Cat 8 cables are backward compatible with older Cat standards, you won’t achieve the full 40 Gbps speed unless your network equipment (switches, routers) also support Cat 8.
Need:
For most home users and even some small businesses, Cat 5e or Cat 6 cables are likely sufficient to handle current internet speeds and network demands. Cat 8 is really targeted towards high-performance applications and future-proofing for businesses with heavy network traffic.
6. Cat 6 vs Cat 6a vs Cat 7 vs Cat 8: FAQ
Q: Is Cat 8 Overkill?
Cat 8 is likely overkill for most situations. It’s super fast, but expensive. For home use or even some businesses, Cat 5e or Cat 6 is enough for current speeds. Cat 8 is best for data centers or future-proofing high-traffic networks. We can help you decide which type of cable is best for your situation.
Q: Do Cat 9 Cables Exist?
Q: Can I Plug a Cat 8 Cable Into a Cat 6 Jack?
Yes, a Cat 8 cable will physically fit into a Cat 6 jack. Think of it like a wider plug fitting into a slightly narrower outlet.
But, the Cat 6 jack won’t give you the super-fast speeds a Cat 8 cable is capable of. It’s like having a high-performance car stuck on a slow road.
Q: Can I Mix Cat6 and Cat8 Cables?
Yes, you can mix Cat6 and Cat8 cables in your network. They’ll work together, but your speed will be limited to the slower cable (Cat6 in this case). It’s like using a high-speed car on a regular road – you won’t get the full benefit of the faster cable.

For Cat 6 vs Cat 6a vs Cat 7: Trust Network Telecom
You can trust Network Telecom to offer your business expert advice and answer any questions you may have when it comes to Ethernet networks, cabling, and telecommunications. We can help you further understand any questions you may have about Cat 6 vs Cat 6a vs Cat 7 cables and help you determine the best one for your needs.
Our team of experts is here to help. Network Telecom has decades of experience providing businesses in the Kitchener-Waterloo, Cambridge, and Guelph regions with the best possible telecommunications solutions.
In addition to our accredited and certified technical expertise, we offer:
Contact us today for all of your telecommunication questions and concerns; we’d be happy to help you.



