When you need to connect multiple wired devices like computers, printers, and IP phones, but only have one Ethernet wall port, using an Ethernet splitter or network switch can expand your connectivity without rewiring.
This guide explains your options and helps you choose the best solution for your setup. Click on each section to learn more.
What Is an Ethernet Splitter?
Five Ways to Split an Ethernet Connection
- Use an Ethernet Network Switch
- Use an Ethernet Hub
- Use a Ethernet Splitter Cable
- Use an Ethernet Cable Sharing Kit
- Use a Router
Choosing the Right Option
Troubleshooting Common Ethernet Splitter Problems
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When to Call a Professional
If you are setting up a home office or a new business and you need help with the cabling or wireless network set-ups, contact us.
We have over 40 years of cabling/wiring experience and we can do the installation professionally and reliably, so you won’t have to worry about unnecessary downtime.
Key Takeaways
- Overview & Purpose: Explains how to expand a single Ethernet connection to multiple devices using splitters, switches, hubs, or routers
- Best Option – Network Switch: Recommends using a network switch because it uses packet‑switching, which directs data only to the intended device—maintaining full speed
- Hub Trade-offs: Covers hubs, noting they broadcast data to all devices (slowing network performance) and are largely outdated
- Splitter Cable Use Case: Describes a basic splitter cable that physically connects two devices but allows only one to transmit at a time—best for occasional device swapping
- Ethernet Sharing Kit: Details a kit with dual adapters that combines two router ports into one cable, then splits them at the other end without noticeable speed loss—great for two‑device setups
- Router-as-Splitter: Mentions using an extra router as a splitter, though a switch is often simpler and cheaper
- Pro Tip: Ends with a suggestion to hire Network Telecom’s professional team for expert network cabling and setup in business environments
What Is an Ethernet Splitter?
An Ethernet splitter is a simple, cost-effective device that allows two different network connections to share a single Ethernet cable over a limited distance. This tool can be useful for minor setups where running a second cable is impractical, but it is critical to understand its limitations before deployment.
How Splitters Function and Why They Are Used
Splitters work by utilizing the eight wires inside a standard Category 5e (or better) Ethernet cable, which are typically wired as four pairs.
A standard modern Ethernet connection (100 Mbps or 1000 Mbps) only uses four of these eight wires (two pairs) for data transmission, while the remaining four wires are often left unused.
Ethernet Sharing Kit Setup
An Ethernet splitter kit consists of two separate adapters: one connects to the router/switch and one connects to the receiving devices. The first adapter combines the signals from two distinct network ports onto the four active and four unused wires of the single cable.
The second adapter then separates these two signals back into two standard Ethernet jacks at the far end, allowing two devices to connect.
The effectiveness of using a splitter relies on the connection speed:
- Ethernet splitters can only transmit data at a maximum speed of 100 Mbps, as they restrict each of the two connections to two pairs of wires, which is the physical limitation for 100BASE-T Ethernet.
- Splitters cannot be used to achieve gigabit speeds (1000 Mbps) because gigabit Ethernet requires all four pairs of wires for full-speed transmission.
- They are not the same as a network switch, which actively manages data packets and can route full gigabit speed to multiple devices using only one wall port.
- Splitters offer a quick solution for adding a second network connection without running a new cable, but they trade maximum speed for convenience.
Limitations of Ethernet Splitters
While affordable, splitters have significant functional limitations that make them unsuitable for high-speed or large-scale networks.
- Maximum Speed is Capped at 100 Mbps: Both devices connected via the splitter kit will have their maximum theoretical speed limited to 100 megabits per second, even if the router and devices are capable of gigabit (1000 Mbps) speeds.
- Requires a Full Kit: A splitter only works when paired with a matching adapter at the other end of the cable; simply connecting one splitter to a router and the other end to a single device will not work.
- Uses Two Router Ports: The setup consumes two Ethernet ports on your primary router or switch to combine the signals onto the single shared cable.
- Not a Replacement for a Network Switch: Splitters are a passive solution that share cable bandwidth, whereas a switch is an active device that uses intelligence to manage and route data traffic efficiently.
It is important to remember that for any application requiring speeds over 100 Mbps, like streaming 4K video or transferring large files, a dedicated network switch or a second cable run will be required.
Five Ways to Split an Ethernet Connection
When you need to connect multiple wired devices but only have a single Ethernet port available, there are several ways to expand your connection. The chart below provides a quick comparison of five common methods.
| Method | Number of Devices Supported | Speed Impact | Ease of Setup | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network Switch | 4–48+ | None (Full speed maintained) | Easy | Home offices, small businesses |
| Ethernet Hub | 4–8 | Significant slowdown | Easy | Legacy networks only |
| Splitter Cable | 2 | Only one active at a time | Very easy | Device swapping convenience |
| Sharing Kit | 2 | Minimal impact | Moderate | Two devices, long cable runs |
| Router | 4+ | Minimal | Moderate | When a spare router is available |
Splitter for Ethernet Cable
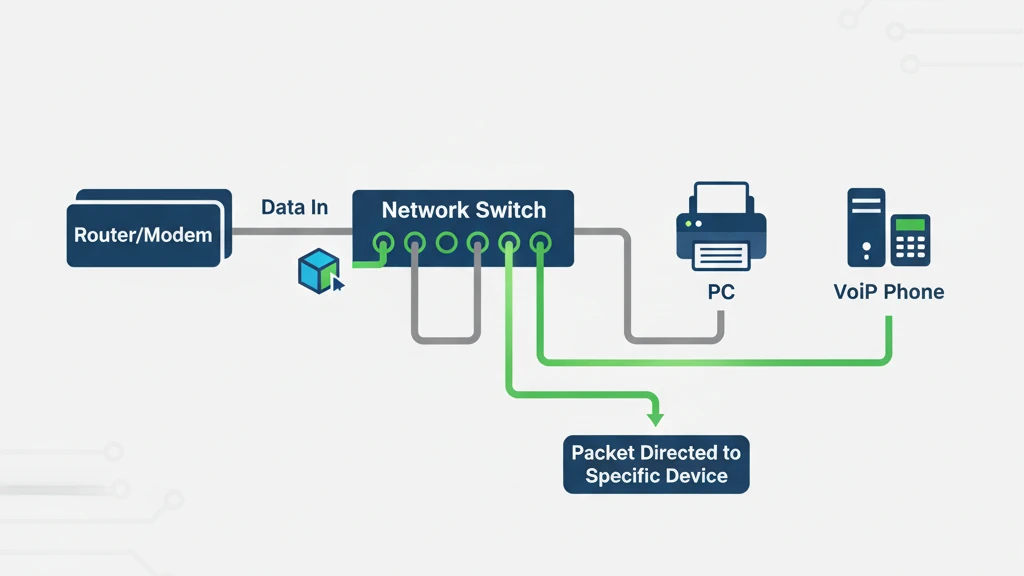
1. Use an Ethernet Network Switch
A network switch is a very effective splitter for ethernet cable.
One of the easiest ways to operate multiple devices off of one ethernet connection is by using a network switch. A network switch will let you connect your ethernet cable from your router or modem at one end to the other devices that you want to connect on the other end of your cable.
Step 1: Plug in your ethernet cable into the ethernet input port on your network switch.
Step 2: Plug in the other devices that you want to share the ethernet connection into the other ports on the switch.
Step 3: Plug in the power cord for your network switch and turn it on.
The network switch will use a process called packet switching. This is a very effective way to transfer a packet of data from more than one device through a single ethernet cable. The data is sent only to the devices that need them.
It is a similar process to making a two-way phone call on a shared phone line. Only the caller and the receiver hear each other and not all the other phones connected to the line. Because only the devices that are using the information packet, receive the information, your network speed doesn’t slow down.
2. Use an Ethernet Hub
An ethernet hub will be slow if you have multiple devices connected.
An ethernet hub is another type of splitter for ethernet cable, however, it is an older technology and isn’t as efficient as using a network switch. The ethernet hub looks similar to a network switch and the steps for setting it up are similar.
Step 1: Plug in your ethernet cable into the ethernet input port on your hub.
Step 2: Plug in the other devices that you want to share the ethernet connection into the other ports on the hub.
Step 3: Plug in your ethernet hub.
Ethernet hubs do not use packet switching like network switches do. Instead, they send all of the data to all of the devices connected to the ethernet cable at the same time. This method can clog up your network and really slow down the speed.
If you have a lot of devices on your network, then you probably won’t want to use this method. If you only want to use a couple of devices, then this could still be an option for you as there won’t be that much traffic on your network.
3. Use a Ethernet Splitter Cable
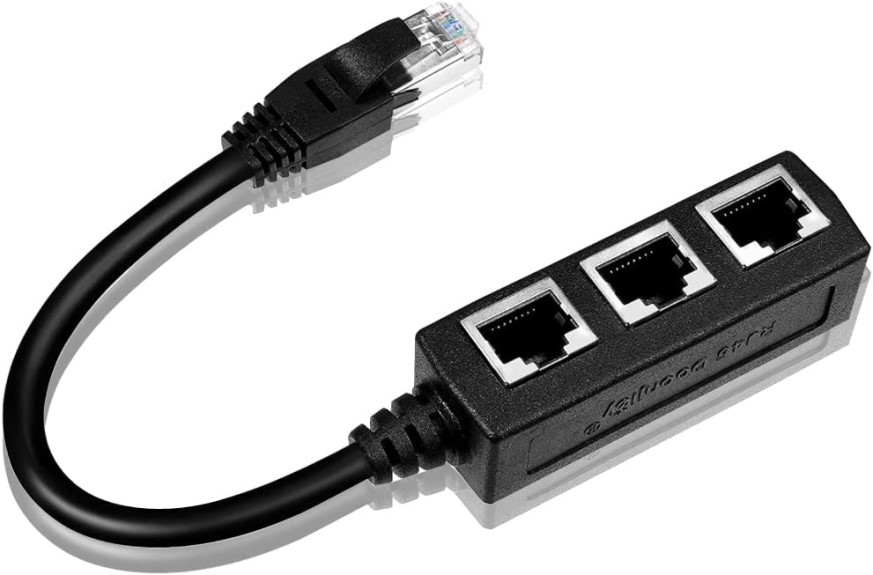

An ethernet splitter cable only lets you physically connect two devices.
One other type of a splitter for ethernet cable is called an ethernet splitter cable. This device only lets you physically connect two devices to the same ethernet cable. However, even though the devices are connected to the cable, only one device can transfer data at one time.
So, in effect, the only advantage of the splitter cable is that it will save you the time and effort of having to physically unplug your ethernet cable from one device and plug it into another to use it.
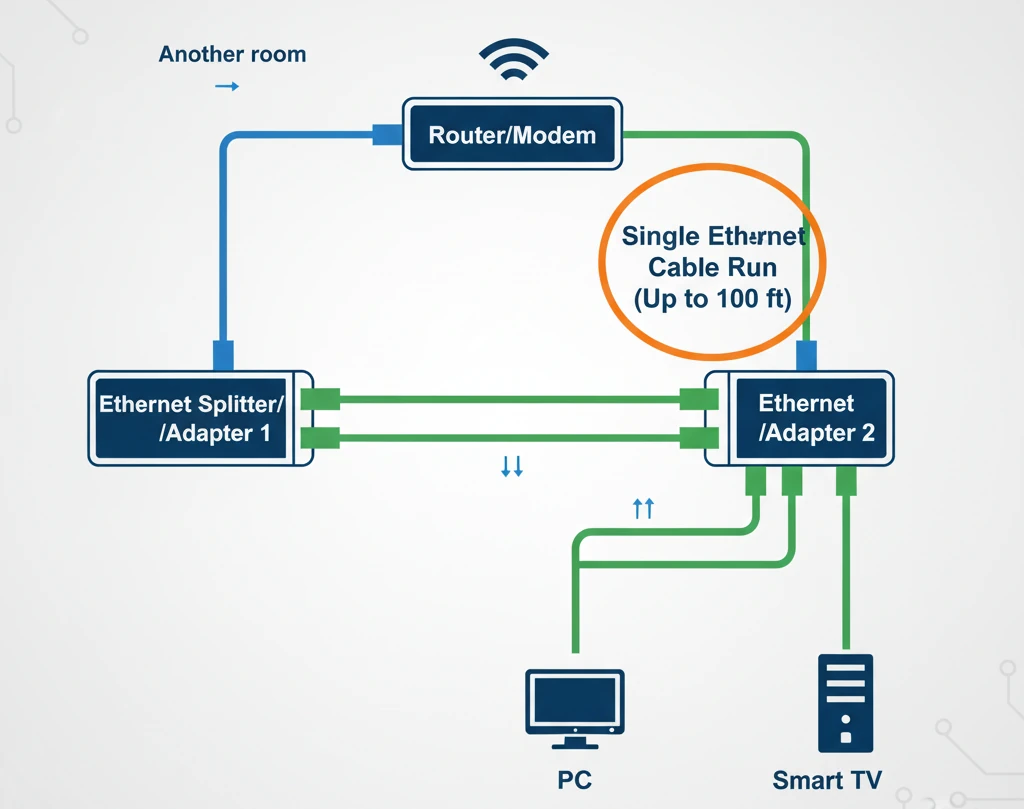
4. Use an Ethernet Cable Sharing Kit
An ethernet sharing kit can be used if you only need to have 2 devices sharing your ethernet cable. In essence, it reduces the two connections from your router into one ethernet cable and then re-expands the one ethernet cable back into two connections in a different part of your office.
If you need to use more than 2 devices, you should use a network switch instead.
An ethernet sharing kit will let you run two devices very smoothly on the same ethernet cable with no noticeable speed decreases.
Your ethernet cable sharing kit should include: 2 adapters. The first adapter will have 2 input ethernet ports and 1 output ethernet port. The second adapter will have 1 input ethernet port and 2 output ethernet ports.
Step 1: Connect your first adapter’s two inputs into two ports on your router
Step 2: Connect your first adapter’s one output to your single ethernet cable.
Step 3: Connect your second adapter’s one input to the other end of your ethernet cable.
Step 4: Connect your second adapter’s two outputs into the two devices that you want to share the ethernet connection.
Even though the set up may seem a bit more challenging, it will let you run your two devices very smoothly on the same ethernet cable with no noticeable speed decreases.
5. Use a Router
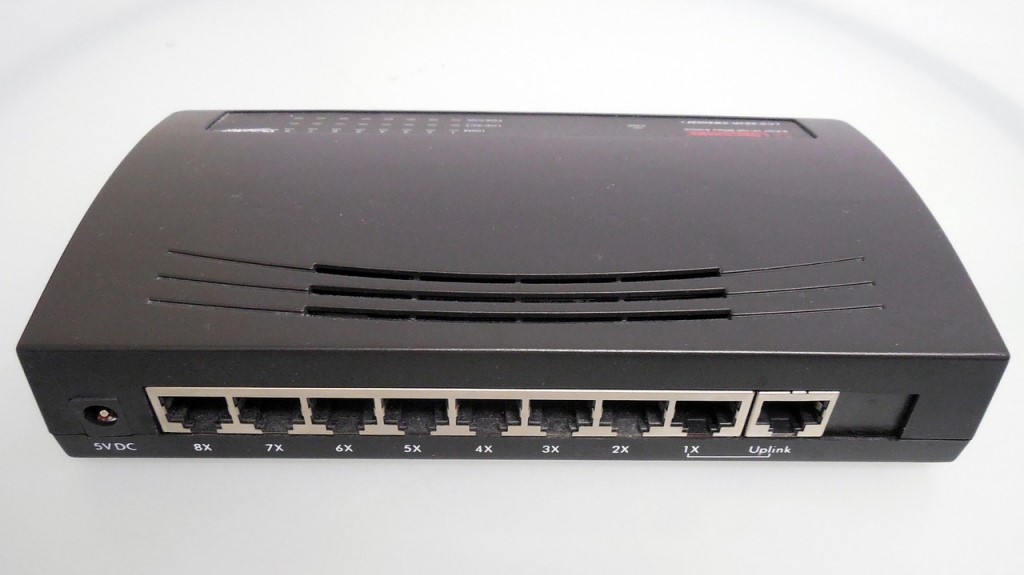

A router can serve as a splitter for ethernet cable.
A final type of splitter for ethernet cable is a router. You can actually use a router instead of a network switch.
Step 1: Connect your ethernet cable into the input port on your router.
Step 2: Connect the devices you want to use into the rest of the extra ethernet ports on your router.
Step 3: You may need to any firewalls and DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) so that your router will run faster.
This method is a good solution is you already have an extra router that you are not using. If you have to purchase one, then you will probably find it less expensive to purchase a network switch.
Choosing the Right Option
Not all Ethernet splitters and connection methods work the same way. The best option for your setup depends on how many devices you need to connect, how fast you need your network to be, and how simple you want the installation process to remain. Use the guide below to help you decide which solution fits your needs.
🟩 Use a Network Switch if You Need Speed and Reliability
A network switch is the most efficient and scalable solution for splitting your Ethernet connection.
- A switch maintains full network speed because it sends data only to the intended device.
- It can support several devices at once making it perfect for offices, gaming setups, or smart homes.
- Installation is simple: just plug it in and connect your devices.
If you want professional-grade performance with no slowdown, a network switch is almost always the right choice.
🟨 Use an Ethernet Hub for Older or Low-Demand Setups
Ethernet hubs are a basic option that work by broadcasting data to every connected device.
- Hubs can connect multiple devices but share the same bandwidth across all of them.
- They are inexpensive but can cause lag and network congestion when several devices are active.
- They are best reserved for legacy equipment or temporary test networks.
Because hubs use older technology, most users will get better results with a modern switch instead.
🟦 Use an Ethernet Splitter Cable for Simple Device Swapping
An Ethernet splitter cable is a convenient but limited solution.
- It allows two devices to share one Ethernet cable, but only one device can transmit data at a time.
- It’s ideal if you only need to switch between two devices without unplugging and reconnecting cables.
- No power or configuration is required, making it the easiest option to set up.
If you just need occasional connectivity for two nearby devices, a splitter cable can save time and effort.
🟧 Use an Ethernet Sharing Kit for Two Devices Over One Cable Run
A sharing kit lets you run two Ethernet connections through a single cable without losing speed.
- It uses paired adapters to combine two signals on one cable and separate them again at the other end.
- It’s a good choice when you want to connect two devices across a long cable run without adding new wiring.
- Installation is straightforward once both adapters are connected properly.
For simple two-device setups, a sharing kit offers a practical balance between performance and convenience.
🟥 Use a Router When You Have an Extra One Available
If you already have a spare router, you can repurpose it as a splitter.
- A router provides additional Ethernet ports and can manage network traffic effectively.
- Configuration may involve adjusting DHCP or firewall settings for smooth operation.
- It’s a cost-effective solution if you have unused equipment, but overkill for small setups.
When configured correctly, a router can perform a similar role to a switch while adding extra network management features.
Each of these methods can expand your wired network, but they differ in performance, price, and practicality. For most users and businesses, a network switch remains the best all-around option for reliable, high-speed Ethernet connectivity.
Troubleshooting Common Ethernet Splitter Problems
Even with the right hardware, Ethernet connections can sometimes run into issues. Understanding common problems and how to address them can save time and prevent network frustration. The tips below cover the most frequent challenges users encounter when using splitters, switches, hubs, and sharing kits.
🟩 Connection Drops or Intermittent Signal
Connection drops can interrupt work or slow down important network tasks.
- Check all cable connections to ensure they are fully plugged in and seated correctly.
- Inspect cables for visible damage or wear, as faulty cables can cause intermittent connectivity.
- Restart your switch, hub, or router to reset the network and resolve temporary glitches.
Regularly checking connections and using high-quality cables can reduce the likelihood of dropped signals.
🟨 Slow Network Speeds
Slow speeds are common when multiple devices share a single connection.
- If you’re using a hub, consider upgrading to a network switch to maintain full speed for each device.
- Limit the number of devices actively transmitting data at the same time if using a splitter cable or sharing kit.
- Ensure your network devices support the same speed standard (e.g., Gigabit Ethernet) for optimal performance.
Addressing speed issues early helps prevent bottlenecks that can impact business operations or home streaming.
🟦 Incorrect Cable Pairing or Adapter Setup
Misconfigured adapters or splitters can prevent devices from connecting properly.
- Verify that the input and output ports on a sharing kit or splitter are correctly connected.
- Check the device manual for proper adapter orientation and port assignment.
- Label cables if multiple runs exist to avoid accidental swaps that can disrupt the network.
Properly configuring each device ensures your Ethernet splitter setup functions reliably.
🟧 Power or Configuration Issues on Switches and Routers
Some Ethernet devices require power or settings adjustments to work correctly.
- Make sure switches and routers are connected to a power source and powered on.
- For routers used as splitters, verify DHCP and firewall settings to avoid IP conflicts.
- Firmware updates on switches and routers can resolve known connectivity or performance issues.
By maintaining power and proper configuration, you can avoid most common network interruptions.
Troubleshooting these common issues can help you maintain a stable and fast Ethernet network. If problems persist, consulting a professional can ensure your network is set up correctly and running smoothly without unnecessary downtime.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Adding an Ethernet splitter or expanding your wired network raises common questions. Below are answers to help you understand your options and make the best choice for your setup.
When to Call a Professional
Setting up an Ethernet splitter or expanding your wired network can sometimes be straightforward, but there are situations where professional help ensures your network runs reliably and efficiently. The points below highlight scenarios where contacting an expert is the best option.
🟩 Complex Network Setup or Large Installations
Large offices or multi-device setups can quickly become complicated.
- If your network involves many devices, switches, or long cable runs, a professional can design an optimal layout to prevent bottlenecks.
- Complex setups may require configuring VLANs, IP assignments, or firewalls to ensure smooth operation.
- Professionals can perform site surveys to determine the best cable paths and avoid interference from electrical or structural obstacles.
Hiring an expert at this stage prevents costly mistakes and ensures all devices operate at maximum efficiency.
🟨 Troubleshooting Persistent Network Issues
Some problems are difficult to resolve without experience.
- Repeated connection drops, slow speeds, or intermittent signals may indicate deeper network issues.
- Incorrect router or switch configurations can cause conflicts that are tricky to diagnose.
- Professionals have the tools and knowledge to quickly identify and resolve issues that may take hours for a DIY setup.
Calling a technician saves time and reduces frustration when common fixes don’t solve the problem.
🟦 Upgrading or Expanding Your Network
Expanding an existing network can introduce new challenges.
- Adding additional switches, hubs, or Ethernet runs may require reconfiguring the network for optimal performance.
- Integrating new devices with older equipment can create compatibility or speed issues.
- A professional ensures that all devices communicate correctly and that network speed is maintained.
Expert guidance ensures your network grows seamlessly without compromising performance or security.
For reliable, efficient, and professionally installed Ethernet networks, contact Network Telecom today. Our certified technicians have over 40 years of experience in cabling, networking, and telecommunications.
Call 519-578-2100 or Request a Quote
to have your network installed or optimized with minimal disruption to your business.
For Help Cabling/Wiring Your Business or Office, Contact Network Telecom

If you need cabling installed or wireless networks set up, we can help. Installing cables for your business or home office may not be a straightforward process. To ensure that it is done properly and with minimal disruption to your work, it is best to have a professional company do it for you.
A professional will have the expertise to advise you on your optimal set up and will have the required knowledge to troubleshoot any issues that may come up.
Don’t risk downtime or unstable connections. Network Telecom’s certified technicians can design, install, and optimize your wired and wireless networks for seamless performance.
At Network Telecom, we have extensive experience in all areas of telecommunications including cabling, and networking. We can easily install and set up any type of network that you require. Contact us today to learn more.
Whatever your business telecommunications needs are, Network Telecom is here for you. We have been selling, installing, and servicing every type of phone system for over 40 years. We can even help with training your employees on the features of your new phone system so that you can use it as efficiently as possible.
If your phone system is not working as it should, our trained technicians are available to help 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year. We carry a huge selection of parts in order to quickly solve any component issues you are experiencing.

Proudly serving businesses across Kitchener, Waterloo, Cambridge, and Guelph for over 40 years.

In addition to our accredited and certified technical expertise, we offer:
- Consultative Sales
- Cloud Services
- Ongoing Support
- Voice Mail Systems
- System Design + Consulting
- System Admin + User Training
- PA Systems
- VoIP Specialist
- Network Cabling
“Network Telecom was wonderful to work with. Helpful and knowledgeable, their team transitioned our office to the new phone system with ease. They were also available to answer concerns and provide additional support post transition. Would definitely recommend their services. Thank you to the team at Network Telecom!”
“We just had an installation done today and it was a great experience. I am not at all tech savvy but everything was explained in a helpful and patient manner. The system seems great and we are really looking forward to running a more efficient office. Highly recommended!”
“Outstanding Service! We had a full phone system installed at a brand new facility and the experience was great. From sales to service the team followed through. The support we have received so far has been excellent. During our install the Network Telecom team even stepped in to help another company who couldn’t complete their portion of the install on time. They truly understand the big picture and will do what it takes to ensure the install is completed to keep your business up and running. 10/10”

