Helpful Tips for Developing Your Professional Skills in the Business World
In the business world, professional skills are highly valued and can contribute to your success and the success of your business. Here is a list of some essential professional skills. Click on each one to learn more about each one and to get some great tips to help you develop these skills:
- Communication
- Leadership
- Problem Solving
- Adaptability
- Teamwork
- Time Management
- Emotional Intelligence
- Networking
- Financial Literacy
- Technology Proficiency
If you are looking to improve or update your business communications plataforms, contact us.
1. Communication

Learning how to communicate effectively is one of the key professional skills.
Effective communication skills are crucial in business. Good communication will enable you to do the following more clearly and effectively:
- Collaborate
- Negotiate
- Present your ideas
Good communication includes both verbal and written communication, as well as active listening. Here is a breakdown of each of these skills with tips on how to improve them.
Verbal Communication
Clarity and Conciseness:
Be clear and concise in your verbal communication. Use simple language, avoid jargon, and express your ideas in a well-organized manner. Get to the point and avoid unnecessary details.
Non-Verbal Cues:
Pay attention to your body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice. Maintain eye contact, use appropriate gestures, and speak with confidence and enthusiasm. Non-verbal cues can enhance your message and convey sincerity.
Empathy and respect:
Show empathy and respect towards others’ opinions and perspectives. Be open-minded, consider different viewpoints, and avoid dismissive or confrontational language. Foster a positive and inclusive environment for effective communication.
Preparation and practice:

Take time to practice what you are going to say ahead of time.
Before important discussions or presentations, prepare your thoughts and key points. Practice your delivery to ensure clarity and confidence. Rehearse difficult conversations to handle them with tact and professionalism.
Feedback and self-reflection:
Seek feedback from others to identify areas for improvement. Reflect on your communication experiences, identify strengths, and work on areas that need development. Continuously strive to enhance your communication skills.
Adaptability:
Adjust your communication style based on the situation and audience. Tailor your language, tone, and approach to effectively communicate with different individuals and groups.
Continuous learning:
Stay updated with communication trends, techniques, and best practices. Read books, attend workshops, or take courses on effective communication to further develop your skills.
Written Communication
Know your audience:

Think about who you are writing to before you begin.
Understand who you are communicating with and tailor your message to their needs, knowledge, and expectations. Use appropriate language and tone that resonates with your target audience.
Be clear and concise:
Similar to verbal communication, you also want to be clear and concise in your written communication. Get straight to the point and avoid unnecessary jargon or complex language. Use simple, straightforward sentences to convey your message effectively.
Business emails should be concise and professional. Use a clear subject line, address the recipient appropriately, and include a signature with your contact information.
Organize your content:
Structure your writing in a logical and coherent manner. Use headings, bullet points, and paragraphs to break down information into easily digestible chunks.
Proofread and edit:
Always proofread your writing to catch any errors in grammar, punctuation, and spelling. Editing will help you refine your message and ensure it is professional and polished.
Be professional:
Maintain a formal tone in your business communication, even in emails. Avoid using slang, emojis, or informal language unless it’s appropriate for the specific context. Always maintain a respectful and positive tone in your writing. Avoid using harsh or offensive language and show empathy towards your readers.
Tailor your level of formality to the relationship you have with the recipient. For instance, you might use a more formal tone when communicating with a client compared to an internal colleague.
Start emails and letters with a proper greeting, such as “Dear Mr./Ms.” followed by the recipient’s last name.
Use active voice:

Avoid using the passive voice in your writing.
Using the active voice instead of the passive will make your writing more direct and engaging. This is because the active voice focuses on the subject performing the action rather than the subject being acted upon. The following sentences demonstrate the difference between the active and passive voice:
I wrote an email to my prospective customer. – Active voice
An email was written by me to my prospective customer – Passive voice
Avoid excessive use of acronyms:
While some industry-specific acronyms may be acceptable, overusing them can create confusion for those who are not familiar with them.
Respond promptly:
In the business world, time is valuable. Aim to respond to messages and emails promptly, even if it’s just to acknowledge receipt and indicate that you will provide a detailed response later.
Avoid using all caps:
Writing in all capital letters can be perceived as shouting and is generally considered unprofessional. Use caps sparingly for emphasis.
Active Listening
Give your full attention:

Active listening is a skill you can improve.
Focus on the speaker and avoid distractions. Put away your phone, close other tabs or apps, and maintain eye contact to show that you are fully engaged.
Be present in the moment:
Clear your mind of other thoughts and concerns. Stay in the present and resist the urge to jump ahead or interrupt the speaker. Let the speaker finish their thoughts before responding. Interrupting can be disruptive and may cause the speaker to lose their train of thought.
Show interest and empathy:
Demonstrate genuine interest in what the speaker is saying. Show empathy by acknowledging their feelings and emotions.
Use verbal and non-verbal cues:
Nodding, smiling, and using encouraging verbal cues like “I see” or “I understand” lets the speaker know you are actively listening and encourages them to continue.
Paraphrase and summarize:
Periodically repeat the speaker’s main points in your own words to ensure you understand correctly. Summarizing helps confirm your understanding and shows the speaker that you are attentive.
Ask clarifying questions:

Ask questions to ensure you are understanding what is being said.
If something is unclear or you need more information, ask open-ended questions to gain further insight and show your engagement.
Avoid judgment and assumptions:
Be open-minded and avoid making assumptions about the speaker’s motives or intentions. Listen without judging their ideas or opinions. Stay composed and manage your emotions while listening. If the topic is sensitive or triggering, try to maintain a calm and understanding demeanor.
Avoid planning your response:
Resist the temptation to formulate your response while the speaker is still talking. Instead, focus on fully understanding their message.
Be patient:
Sometimes, the speaker may take their time to express themselves fully or may repeat certain points. Stay patient and give them the space they need to communicate effectively.
Acknowledge the speaker’s feelings:
If the speaker expresses emotions, acknowledge them and let them know you understand how they feel.
Practice active listening regularly:
Like any skill, active listening improves with practice. Make a conscious effort to apply these tips in your conversations regularly.
2. Leadership

Try to develop strong relationships with your teammates – Photo by krakenimages on Unsplash
Developing leadership professional skills in the business world is essential for effectively guiding teams, making strategic decisions, and achieving organizational goals. Here are some tips to help you enhance your leadership skills:
Lead by Example:
Demonstrating the behaviour and work ethic you expect from your team sets a strong precedent. Your actions speak louder than words, so embody the qualities you want your team to embrace.
Communicate Effectively:
Clear and open communication is crucial. Listen actively to your team members, provide feedback, and ensure everyone understands the goals and expectations.
Empower Others:
Delegate tasks and responsibilities, giving your team members the opportunity to develop their skills and take ownership of their work. This fosters a sense of ownership and motivation.
Build Relationships:
Forge strong relationships with your team members based on trust, respect, and empathy. Understand their strengths, weaknesses, and aspirations to better support their growth.
Develop Your Problem-Solving Skills:
Leaders often encounter challenges. Develop your problem-solving skills by approaching issues methodically, considering multiple perspectives, and finding innovative solutions.
Make Informed Decisions:
You can make informed decisions by gathering relevant information, considering potential outcomes, and understanding the implications of your choices on both short-term and long-term goals.
Manage Your Time Wisely:
Efficiently manage your time to balance strategic thinking, team management, and personal development. Prioritize tasks, set deadlines, and avoid micromanagement.
Be Adaptable:
Business environments can change rapidly. Be flexible and adaptable, embracing change while guiding your team through transitions effectively.
Resolve Conflicts Effectively:
Address conflicts promptly and constructively. Focus on the issues at hand, remain neutral, and encourage open dialogue to find mutually beneficial resolutions.
Continue Learning:

Keep learning about new industry trends and management practices. – Photo by Kenny Eliason on Unsplash
Stay up-to-date with industry trends, leadership theories, and management practices. Invest in your personal and professional skills development through workshops, courses, and reading.
Inspire and Motivate:
Paint a compelling vision of the future that inspires your team. Celebrate successes, acknowledge efforts, and motivate team members to go the extra mile.
Provide Feedback:
Cultivate a culture of continuous improvement by providing regular, constructive feedback to your team members. Encourage them to do the same for you.
Mentor:
Mentorship demonstrates your commitment to your team’s growth. Provide guidance, share experiences, and help them develop their skills and careers.
Be Resilient:
Leaders face setbacks and challenges. Develop emotional resilience to maintain a positive attitude and keep moving forward even in tough times.
Be Ethical:
Uphold high ethical standards in your decision-making and interactions. This fosters trust, credibility, and respect among your team and stakeholders.
Network:
Build a strong network within and outside your organization. Networking offers opportunities to learn from others, exchange ideas, and gain insights into different leadership approaches.
Be Self-Aware:
Reflect on your strengths, weaknesses, and leadership style. Self-awareness helps you understand how your actions and decisions impact others.
Remember that leadership skills develop over time through practice, self-reflection, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Be patient with yourself and actively seek opportunities to apply and refine these skills.
3. Problem Solving

Effective problem solving can help you identify, analyze, and address issues that come up – Photo by Yosep Surahman on Unsplash
In today’s dynamic and competitive business environment, the ability to effectively solve problems is a skill that can set you apart from other businesses. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting your career, honing your problem-solving skills is essential for success no matter what industry you operate in. In this section, we’ll explore the importance of problem solving in the business world and provide you with valuable tips to develop and enhance this crucial skill.
A) Recognize the Value of Problem Solving
Understanding why problem solving is so important in the business world is a crucial step toward mastering it. Problems arise in every aspect of business, from daily operations to strategic decision-making.
Being an adept problem solve not only allows you0 to navigate these challenges with ease but also positions you as a valuable asset within your organization. Effective problem solvers are often sought after for leadership roles because they can lead teams to overcome obstacles and achieve goals.
B) Develop a Problem-Solving Mindset
Problem solving is not just about finding quick fixes; it’s a mindset that involves critical thinking, creativity, and resilience. To develop this mindset:
Embrace Challenges:
Instead of avoiding difficult situations, view them as opportunities to learn and grow. Embracing challenges will help you build confidence in your problem-solving abilities.
Stay Curious:
Ask questions, seek to understand root causes, and explore different perspectives. A curious mindset is essential for uncovering innovative solutions.
Be Adaptable:
Recognize that not all problems have one-size-fits-all solutions. Be flexible and open to adapting your approach as you gather more information and insights.
C) The Problem Solving Process
Effective problem-solving in a business context is one of the professional skills that involves a structured approach. This technique will help you identify, analyze, and address challenges while making well-informed decisions. Here’s a step-by-step guide you can follow:
STEP 1: Define the Problem:
Clearly articulate the issue or challenge you’re facing. Break down the problem into specific components, ensuring you understand the scope and context.
STEP 2: Gather Information
Collect relevant data, facts, and information related to the problem. Consult team members, stakeholders, and reliable sources to get a comprehensive view of the situation.
STEP 3: Identify the Root Cause
Dig deeper to uncover the underlying causes of the problem. Use techniques like the “Five Whys” to ask iterative “why” questions and get to the core issue.
STEP 4: Generate Solutions
Brainstorm a range of potential solutions without judgment. Encourage creativity and involve team members with diverse perspectives. Quantity is key at this stage.
STEP 5: Evaluate Solutions
Assess the pros and cons of each solution. Consider factors like feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and potential impact on the organization.
STEP 6: Make a Decision
Select the most viable and realistic solution based on your in-depth evaluation. Be prepared to justify your choice to stakeholders.
STEP 7: Implement and Monitor:
The work does not end once a decision is made. It is now time for you to monitor your chosen solutions progress and make changes if necessary.
D) Effective Communication
Effective communication is a critical component of successful problem solving in the business world. It involves conveying information, ideas, and solutions clearly and persuasively to various stakeholders. Here are some key aspects to consider:
Clarity:
Ensure that your communication is clear and concise. Avoid jargon or overly technical language, especially when explaining complex problems or solutions to your stakeholders or business partners. Use simple and straightforward language to make your points easily understood
Active Listening:
Listening is just as important as speaking. When collaborating with team members or discussing a problem with others, practice active listening. This means giving your full attention to the speaker, asking clarifying questions, and demonstrating empathy.
Tailored Messaging:
Understand your audience and tailor your communication style accordingly. Different stakeholders may have varying levels of expertise and interest in the problem, so adjust your approach to meet their needs. For example, executives may need a high-level summary, while technical teams may require more detailed information.
Transparency:
Be transparent about the problem, the steps taken to address it, and the progress made. Transparency builds trust and ensures that everyone involved is on the same page. You do not want to leave out key details that can come back to bite you in the future.
Conflict Resolution:
Problems can sometimes lead to conflicts within teams or between individuals. As a problem solver, be prepared to mediate and resolve conflicts constructively. Encourage open dialogue and seek win-win solutions when possible. After all, conflict within teams or between individuals can negate productivity and overall satisfaction.
Documentation:
Keep records of important discussions, decisions, and actions taken during the problem-solving process. Proper documentation ensures that there is a clear historical record and helps prevent misunderstandings or disputes in the future.
E) Continuous Learning and Improvement
Problem solving is a skill that can always be refined and expanded. To continuously improve your problem-solving abilities:
Reflect on Past Experiences:
After solving a problem, take the time to reflect on the process. What went well? What could have been done differently? Analyzing past experiences allows you to learn from both successes and failures to ensure you do better in the future.
Seek Feedback:
Ask your colleagues, mentors, or supervisors for constructive feedback. Others may have valuable insights into your problem-solving approach that you may not have considered.
Stay Informed:
Stay up-to-date with industry trends, best practices, and emerging technologies that could impact your problem-solving abilities. Attend workshops, seminars, or online courses to broaden your knowledge.
Mentoring and Coaching:
Consider seeking guidance from experienced problem solvers or mentors in your organization. Given their expertise, they can share their expertise and offer valuable advice on tackling complex issues.
Practice Problem Solving:
Challenge yourself with real-world problems or scenarios outside of your immediate job responsibilities. This could involve participating in cross-functional projects, volunteering for challenging tasks, or joining problem-solving teams.
Encourage a Learning Culture:
Foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement within your organization. Encourage team members to share their problem-solving experiences and insights, creating a collaborative environment for growth.
By focusing on effective communication and embracing a commitment to continuous learning and improvement, you’ll not only enhance your problem-solving skills but also contribute to a culture of innovation and excellence within your professional environment. These aspects are essential for long-term success in the business world.
4. Adaptability
In today’s fast-paced and ever-changing business landscape, adaptability is a prized professional skill. The ability to adjust, evolve, and thrive in the face of shifting circumstances is a key factor in your career success. In this section, we will explore the significance of adaptability in the business world and provide valuable tips to help you develop and strengthen this crucial skill.
A) Understanding the Importance of Adaptability
Before diving into tips for developing adaptability, it’s essential to grasp why this skill is so vital in the business world:
Resilience:
Adaptability is a cornerstone of resilience. In a constantly changing environment, those who can adapt are better equipped to bounce back from setbacks and challenges.
Competitive Edge:
Adaptable professionals are sought after by employers. They can pivot quickly to seize opportunities and navigate uncertainty, making them valuable assets to any organization.
Innovation:
Adaptability often goes hand in hand with innovation. Those who can embrace change are more likely to come up with creative solutions and drive progress within their teams and companies.
B) Tips for Developing Adaptability
Now, let’s explore practical strategies for cultivating adaptability:
Embrace Change as an Opportunity:
Instead of fearing change, view it as an opportunity for growth and learning. Change can lead to new experiences, fresh perspectives, and the chance to acquire new skills.
Stay Informed:
Keep yourself informed about industry trends, market shifts, and emerging technologies. The more you know, the better prepared you’ll be to adapt to changes in your field.
Build a Growth Mindset:
Cultivate a growth mindset, which involves believing that abilities and intelligence can be developed through dedication and hard work. This mindset encourages a willingness to take on challenges and learn from failures.
Develop Resilience:
Resilience is closely tied to adaptability. Strengthen your ability to bounce back from setbacks by developing coping mechanisms, seeking support when needed, and maintaining a positive attitude.
Learn from Experience:
Reflect on past experiences where you’ve had to adapt to change. What worked well? What could you have done differently? Use these reflections to inform your approach to future challenges.
Seek Diverse Perspectives:
Encourage diverse viewpoints and ideas within your team and organization. Different perspectives can lead to more innovative and adaptable solutions.
Flexibility in Problem Solving:
When faced with obstacles, be open to adjusting your approach. Be willing to pivot, revise strategies, and try new approaches as needed.
Network and Collaborate:
Build a strong professional network and collaborate with others in your industry. Networking can provide valuable insights and support during times of change.
Set Realistic Goals:
Establish achievable goals that align with your adaptability efforts. Monitor your progress and celebrate your successes along the way.
C) Adaptable Leaders in Action
One of the most effective ways to understand and appreciate adaptability is to examine real-world examples of leaders and organizations that have successfully demonstrated this skill. By showcasing their experiences, you can provide your readers with practical insights and inspiration for developing their own adaptability. Here are a few examples and ways to present them:
Apple Inc. – Embracing Technological Shifts:
Apple is a prime example of an organization that has consistently embraced and adapted to technological shifts. From its early success with the Macintosh computer to its transformative launch of the iPhone, Apple has shown the ability to pivot and innovate in response to changing consumer preferences and market dynamics.
- Key Takeaway: Apple’s adaptability highlights the importance of staying ahead of industry trends, continuously innovating, and being willing to disrupt the status quo.
Elon Musk – Mastering Multiple Industries:
Entrepreneur and innovator Elon Musk is known for his adaptability in tackling various industries. He co-founded PayPal, ventured into electric vehicles with Tesla, launched SpaceX for space exploration, and even founded Neural-ink and The Boring Company. Musk’s adaptability showcases how a growth mindset and a willingness to tackle diverse challenges can lead to success.
- Key Takeaway: Musk’s journey underscores the power of adaptability, a relentless pursuit of learning, and the ability to pivot between industries with confidence.
Airbnb – Pivoting During a Crisis:
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Airbnb faced a significant challenge as travel came to a halt. However, the company quickly adapted by offering “Online Experiences,” virtual travel activities that allowed hosts to continue earning income. This quick pivot helped Airbnb weather the storm and even thrive in a challenging environment.
- Key Takeaway: Airbnb’s adaptability underscores the importance of swift response and innovation during times of crisis. It demonstrates how companies can find new opportunities in adversity.
In a business world marked by constant evolution, adaptability is a skill that can set you apart and lead to long-term success. Embrace change, foster resilience, and cultivate a growth mindset to become a more adaptable professional. By doing so, you’ll not only navigate challenges effectively but also seize new opportunities and contribute to the innovation and success of your organization.
5. Teamwork

Teamwork improves accountability and productivity! – Photo by Mohamed Hassan from Pixabay
A) The Importance of Teamwork in the Business World
Teamwork is crucial in the business world for several reasons:
Diverse Skill Sets:
Teams often consist of individuals with diverse skill sets and backgrounds. By working collaboratively, team members can leverage each other’s strengths to achieve a common goal, allowing for a more comprehensive and efficient approach to problem-solving and decision-making.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity:
Effective teamwork allows tasks to be divided and conquered, resulting in increased efficiency and productivity. When team members collaborate, they can complete tasks more quickly and effectively than if they were working individually. This can lead to higher quality outputs and faster project completion times.
Enhanced Creativity and Innovation:
Teamwork fosters an environment where diverse perspectives and ideas are shared. Collaborative brainstorming and idea generation can lead to more innovative and creative solutions to complex business problems. By encouraging open communication and the sharing of different viewpoints, teams can develop more effective strategies and approaches.
Improved Problem Solving:
In a team setting, members can pool their knowledge and experiences to address challenges and obstacles more effectively. Different team members may bring unique insights and alternative solutions to the table, enabling the team to identify and resolve issues more efficiently than an individual working alone.
Better Decision-Making:
Teamwork allows for collective decision-making, which often leads to more well-rounded and thoughtful decisions. By considering various perspectives and weighing different options, teams can make informed choices that consider the diverse needs and goals of the organization.
Employee Satisfaction and Engagement:
Encouraging teamwork can foster a sense of belonging and camaraderie among employees, leading to higher job satisfaction and increased employee engagement. When employees feel valued and supported within a team, they are more likely to be motivated and invested in their work, leading to higher overall job performance and retention rates.
Effective Communication:
Teamwork emphasizes the importance of effective communication, which is essential for the smooth operation of any business. Clear and open communication within a team helps to avoid misunderstandings, reduces conflicts, and ensures that everyone is on the same page, working towards shared objectives.
Overall, teamwork promotes a collaborative and supportive work environment, leading to improved outcomes, employee satisfaction, and the overall success of the organization.
B) Tips for Developing and Improving Teamwork
Here are some tips for developing and improving teamwork in the business world:
Establish Clear Goals and Roles:
Clearly define the team’s objectives, roles, and responsibilities to ensure that every team member understands their contributions to the overall goal.
Foster Open Communication:
Encourage open and honest communication among team members. Create a supportive environment where everyone feels comfortable expressing their ideas, concerns, and feedback.
Cultivate Trust and Respect:
Build trust and respect among team members by encouraging collaboration and acknowledging each other’s contributions. Foster a culture of mutual respect and appreciation for diverse perspectives and skills.
Promote Collaboration:
Encourage collaboration and cross-functional teamwork by organizing regular team meetings, brainstorming sessions, and collaborative projects. Emphasize the value of working together toward a common goal.
Provide Constructive Feedback:
Offer constructive feedback to help team members grow and improve. Focus on providing specific, actionable suggestions that can help individuals and the team as a whole to enhance their performance.
Encourage Empathy and Understanding:
Foster an environment of empathy and understanding by encouraging team members to consider each other’s viewpoints and experiences. This can help create a more inclusive and supportive work culture.
Foster a Positive Work Environment:
Create a positive work environment that promotes teamwork and collaboration. Recognize and celebrate team achievements and milestones to boost morale and foster a sense of camaraderie.
Promote Continuous Learning:
Encourage a culture of continuous learning and development within the team. Provide opportunities for skill enhancement, training, and knowledge sharing to help team members stay updated with industry trends and best practices.
Resolve Conflicts Constructively:
Address conflicts promptly and constructively. Encourage open discussions to understand the root causes of conflicts and work towards finding mutually beneficial solutions.
Lead by Example:
Set a positive example for the team by demonstrating teamwork, effective communication, and a commitment to the team’s goals. Encourage a culture of accountability and responsibility.
By implementing these tips, businesses can create a strong and cohesive team that is capable of achieving its goals effectively and efficiently.
C) Teamwork In Action
Here are some real-life examples of great teamwork in the business world:
SpaceX:
SpaceX’s successful launch and operation of the Falcon 9 rocket exemplify effective teamwork in the aerospace industry. The company’s multidisciplinary teams worked together to develop and launch reusable rockets, which significantly reduced the cost of space travel. These teams consisted of:
- Engineers
- Designers
- Technicians
- Support staff
Their collaborative efforts led to the achievement of significant milestones in space exploration and the commercialization of space travel.
Toyota
Toyota’s implementation of the “Toyota Production System” (TPS), also known as Lean Manufacturing, is a prime example of effective teamwork in the manufacturing industry. The TPS emphasizes continuous improvement and employee involvement in the production process. Toyota’s employees work together to:
- Identify and eliminate waste
- Streamline production
- Ensure high product quality
This collaborative approach has enabled Toyota to become a global leader in the automotive industry and has served as a model for many other manufacturing companies worldwide.
Google:
Google’s cross-functional teams have played a significant role in the development of innovative products and services, such as:
- Google Search
- Gmail
- Google Maps
These teams, comprising software engineers, designers, product managers, and marketers, collaborate closely to create user-friendly and cutting-edge technologies. Google’s emphasis on fostering a collaborative and creative work culture has led to the development of numerous successful products and services that have transformed the way people interact with information and technology.
These examples highlight how effective teamwork, collaboration, and a shared vision can drive:
- Innovation
- Success
- Breakthroughs in various industries
By leveraging the diverse skills and expertise of team members, these companies have been able to achieve remarkable accomplishments and make significant contributions to their respective fields.
6. Time Management

Effective time management is a crucial skill to have in the business world.
A) The Importance of Time Management in the Business World
Time management is a critical skill in the business world, and its importance cannot be overstated. Here is why:
Increased Productivity:
Time management helps individuals prioritize tasks and focus on high-priority activities. This results in increased productivity as people can allocate their time to tasks that contribute the most value to the business.
Meeting Deadlines:
In the business world, deadlines are common and often non-negotiable. Effective time management ensures that tasks are completed on time, reducing the risk of missed deadlines and the negative consequences associated with them.
Reduced Stress and Burnout:
Poor time management can lead to stress and burnout, negatively impacting both mental and physical health. By allocating time wisely and avoiding procrastination, individuals can maintain a healthier work-life balance and reduce stress levels.
Effective Goal Achievement:
Businesses set goals and objectives to measure success. Time management is instrumental in working toward and achieving these goals. By breaking down larger tasks into smaller, manageable steps, individuals can make steady progress toward their objectives.
Improved Work-Life Balance:
Time management is not only about work tasks but also about achieving a balance between professional and personal life. Striking this balance helps prevent burnout, improves overall well-being, and allows individuals to sustain high levels of productivity in the long term.
In summary, time management is a fundamental skill that contributes to individual and organizational success in the business world. It enables individuals to prioritize, plan, and execute tasks efficiently, leading to increased productivity, better decision-making, and a more positive work environment.
B) Tips for Developing and Improving Time Management
Developing and improving time management skills is an ongoing process that can greatly enhance your productivity and overall effectiveness. Here are some practical tips to help you manage your time more efficiently:
Prioritize Tasks:
Use methods like the Eisenhower Box to categorize tasks into:
- Urgent/important
- Important/not urgent
- Urgent/not important
This method is great because it allows you to focus on high-priority tasks first.
Create a To-Do List:
Make a daily or weekly to-do list. Break down larger tasks into smaller, manageable steps. Tick off completed tasks to give yourself a sense of accomplishment.
Use a Time Management Tool:
Consider using tools and apps such as:
- Calendars
- Task management apps
- Project management software
These will allow you to organize and prioritize your tasks better.
Set Realistic Deadlines:
Be realistic about how long tasks will take and set deadlines accordingly. Avoid overcommitting and causing unnecessary stress.
Learn to Say No:
Understand your limits and don’t be afraid to decline additional tasks if your plate is already full. Saying no when necessary is crucial for effective time management.
Reflect and Adjust:
Regularly reflect on your:
- Goals
- Achievements
- Challenges
Adjust your time management strategies as needed to align with changing priorities and circumstances.
Remember that effective time management is a personal process, and what works for one person may not work for another. Experiment with different techniques, and tailor your approach to suit your unique preferences and work style. Consistency and a willingness to adapt are key to developing strong time management skills.
C) Time Management In Action
Many successful individuals in the business world are known for their effective time management skills. Here are a few examples:
Tim Cook (CEO of Apple Inc.):
Tim Cook is recognized for his disciplined approach to time management. He:
- Starts his day early
- Sends out emails early in the morning
- Maintains a well-organized schedule
Cook is known for delegating tasks efficiently and emphasizing the importance of focused work.
Bill Gates (Co-founder of Microsoft):
Bill Gates is not only a tech visionary but also a proponent of effective time management. He is known for his use of the “Think Week,” during which he takes a week off to read and reflect without distractions. Gates is also a fan of the “Five-Hour Rule,” where he dedicates at least five hours per week to learning and personal development.
Mark Zuckerberg (Co-founder and CEO of Facebook):
Mark Zuckerberg is known for his disciplined approach to time management. He follows a consistent daily routine which includes:
- Morning workouts
- Focusing on key priorities
- Setting clear goals
- Staying dedicated to long-term objectives
It is no wonder why Mr. Zuckerberg is so successful.
These examples illustrate that effective time management is a common trait among successful business leaders. Whether through structured scheduling, prioritization, or delegation, these individuals have demonstrated how managing time efficiently contributes to their achievements in the business world.
7. Emotional Intelligence
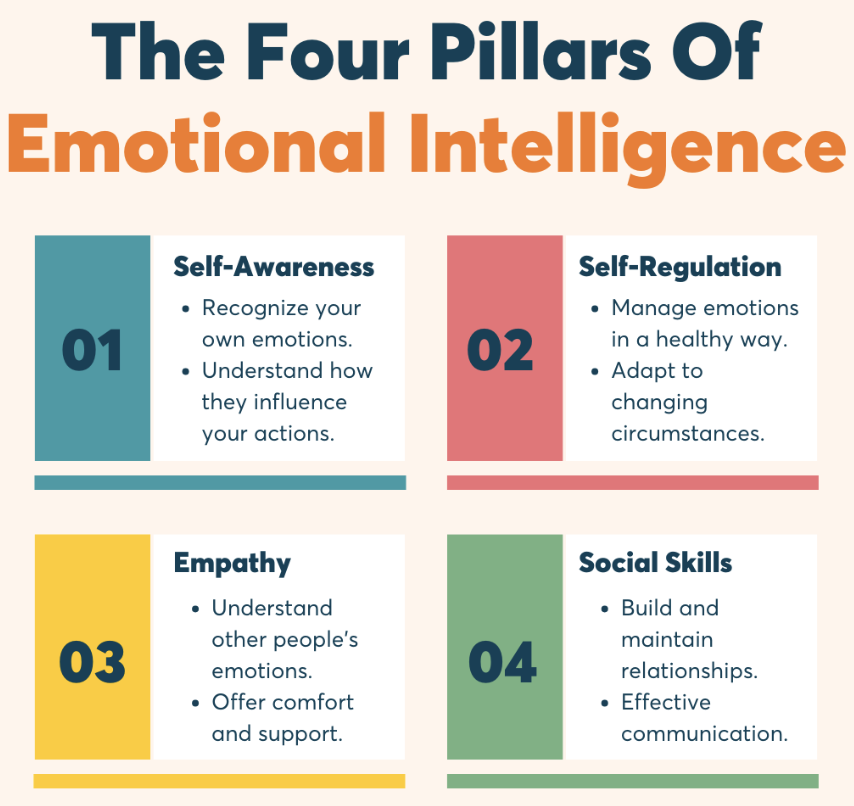
The four pillars of emotional intelligence – Image by Wellable
A) The Importance of Emotional Intelligence in the Business World
Emotional intelligence (EI) is a crucial aspect of success in the business world, influencing various aspects of professional life. EI refers to the ability to recognize, understand, manage, and use one’s own emotions effectively, as well as the ability to perceive and influence the emotions of others. Here are several reasons why emotional intelligence is important in the business world:
Effective Leadership:
Leaders with high emotional intelligence are better equipped to understand and connect with their team members. They can:
- Empathize with others
- Build trust
- Communicate in a way that motivates and inspires
In return, this fosters a positive and collaborative work environment.
Conflict Resolution:
Conflict seems to be inevitable in any workplace. Employees with high emotional intelligence can navigate conflicts more effectively by remaining calm, and empathetic, and finding solutions that satisfy all parties involved. This contributes to a healthier and more harmonious work environment.
Adaptability and Resilience:
The business environment is dynamic and often unpredictable. Those with emotional intelligence are better equipped to:
- Adapt to change
- Manage stress
- Bounce back from setbacks
This resilience is a valuable asset in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
Self-Awareness and Self-Regulation:
Individuals with high emotional intelligence have a strong sense of self-awareness and understanding of their:
- Strengths
- Weaknesses
- Emotional triggers
This self-awareness allows them to regulate their emotions effectively, preventing impulsive or destructive behaviour in the workplace.
Client and Customer Relations:
Understanding and responding to the emotions of clients and customers is crucial for building positive relationships. Individuals with high emotional intelligence can effectively gauge and meet the needs of clients, resulting in increased satisfaction and loyalty.
In summary, emotional intelligence is a key factor in building strong interpersonal relationships, effective communication, and successful leadership in the business world. It contributes to a positive workplace culture, enhances collaboration, and ultimately leads to improved individual and organizational performance. As a result, many successful leaders and organizations recognize the importance of fostering emotional intelligence among their teams.
B) Tips For Developing and Improving Emotional Intelligence
Developing and improving emotional intelligence in the business world is an ongoing process that involves self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy, and effective interpersonal skills. Here are some tips to help you enhance your emotional intelligence in a professional context:
Increase Self-Awareness:
Regularly reflect on your own emotions, recognizing how you feel in various situations. Pay attention to your reactions and triggers. Journaling can be a helpful tool for self-reflection.
Practice Active Listening:
Focus on fully understanding what others are saying without interrupting. Give them your full attention, and demonstrate that you are engaged by paraphrasing or asking clarifying questions.
Develop Empathy:
Put yourself in others’ shoes and try to understand their:
- Perspectives
- Feelings
- Needs
Acknowledge and validate their emotions, even if you don’t necessarily agree with them.
Improve Non-Verbal Communication:
Be mindful of your:
- Body language
- Facial expressions
- Tone of voice
Non-verbal cues can convey a lot about your emotions and intentions. Ensure your non-verbal signals align with your intended message.
Seek Constructive Feedback:
Request feedback from colleagues or mentors on how you handle emotions in the workplace. Use this feedback as an opportunity for growth and improvement.
By actively working on these tips, you can enhance your emotional intelligence and cultivate a more positive and effective presence in the business world. Remember that developing emotional intelligence is a gradual process, and consistent effort over time will yield positive results.
C) Emotional Intelligence In Action
Emotional intelligence (EQ) is a crucial skill in the business world, and many successful individuals have used it to their advantage. Here are some real-life examples:
Steve Jobs:
The late co-founder of Apple, Steve Jobs, was known for his exceptional emotional intelligence. Despite his demanding leadership style, Jobs had a keen understanding of people’s motivations and emotions. He could inspire and motivate his team by tapping into their passion and creativity.
Indra Nooyi:
Former CEO of PepsiCo, Indra Nooyi, is often praised for her emotional intelligence. She is known for her ability to:
- Connect with people on a personal level
- Create a positive work culture
Nooyi’s empathetic leadership style contributed to her success in steering PepsiCo through significant changes during her tenure.
Satya Nadella:
Microsoft’s CEO, Satya Nadella, is recognized for his focus on empathy and emotional intelligence. Under his leadership, Microsoft has experienced a cultural transformation. Nadella emphasizes the importance of understanding customers and employees on a deeper level to drive innovation and collaboration.
These examples demonstrate how emotional intelligence can be a powerful asset in leadership, decision-making, and relationship-building within the business world. Leaders who understand and leverage emotional intelligence effectively often create more positive and productive work environments.
8. Networking

Networking opens the door to endless new business opportunities.
A) The Importance of Networking in the Business World
Networking is crucial in the business world for several reasons:
Business Opportunities:
Networking provides a platform for individuals to meet and connect with:
- Potential clients
- Customers
- Partners
- Investors
- Other key stakeholders
Building strong relationships through networking can lead to new business opportunities, collaborations, and partnerships.
Knowledge and Information Sharing:
Networking allows professionals to exchange:
- Ideas
- Industry trends
- Valuable information
By connecting with others in the same or related fields, individuals can stay informed about the latest developments, best practices, and emerging technologies, helping them make informed decisions in their business activities.
Career Advancement:
Building a strong professional network can enhance career prospects. Networking provides access to mentorship, advice, and guidance from experienced professionals. It can also open doors to:
- Job opportunities
- Promotions
- Career development
This is because many positions are filled through referrals and recommendations.
Brand Visibility and Credibility:
Active participation in networking events and platforms helps in building your personal and professional brand. By showcasing your expertise and contributions, you can enhance your credibility in the industry. Positive word-of-mouth and recommendations from your network can significantly contribute to your professional reputation.
Problem Solving and Support:
In the business world, challenges and problems are inevitable. Networking provides a support system where professionals can:
- Seek advice
- Share experiences
- Collaborate to find solutions
Having a diverse network allows individuals to tap into a variety of perspectives and expertise when facing business challenges.
In summary, networking is a powerful tool for establishing and nurturing relationships that can lead to numerous benefits, including business growth, career advancement, knowledge sharing, and problem-solving. It’s a strategic investment in both personal and professional development in the dynamic landscape of the business world.
B) Tips for Developing and Improving Networking
Here are some tips for developing and improving networking:
Define Your Goals:
Clarify your networking objectives. Having clear goals will guide your efforts and help you focus on building the right connections that align with your professional aspirations.
Attend Relevant Events:
Actively participate in
- Industry conferences
- Seminars
- Networking events
These gatherings provide targeted opportunities to meet professionals in your field, stay updated on industry trends, and expand your network.
Perfect Your Elevator Pitch:
Craft a concise and compelling elevator pitch that succinctly introduces:
- Who you are
- What you do
- What you’re seeking
A well-crafted pitch helps you make a strong first impression and quickly communicate your value.
Actively Listen:
Practice active listening during conversations! This means:
- Pay attention to others
- Ask thoughtful questions
- Show genuine interest in their experiences
This not only fosters a deeper connection but also helps you understand the needs and perspectives of your contacts.
Follow Up:
After meeting new contacts, follow up promptly with a personalized message expressing your pleasure in connecting. This step is crucial for reinforcing the initial connection and sets the stage for further engagement.
Remember, effective networking is about building genuine, mutually beneficial relationships over time. It’s not just about what you can get, but also about what you can contribute to others. Keep refining your networking skills, be authentic, and foster meaningful connections in your professional journey.
C) Networking In Action
Many successful individuals in the business world have attributed their success, at least in part, to effective networking. Here are a few real-life examples:
Bill Gates:
Co-founder of Microsoft, Bill Gates, is known for his extensive networking efforts. In the early days of Microsoft, he actively sought out opportunities to:
- Meet with industry leaders
- Attend conferences
- Build relationships
His networking skills played a significant role in the success of Microsoft.
Oprah Winfrey:
Media mogul Oprah Winfrey is a master networker. She has built a vast network of influential people in various industries, from entertainment to business and philanthropy. Oprah’s ability to connect with people has not only contributed to her own success but has also allowed her to create a powerful network that spans different sectors.
Warren Buffett:
Legendary investor Warren Buffett attributes a significant portion of his success to networking. Despite being an introvert by nature, Buffett recognized the importance of building relationships early in his career. His ability to connect with influential figures in finance and business played a crucial role in the growth of Berkshire Hathaway.
These examples highlight how effective networking can contribute to career growth, business success, and the ability to navigate challenges in the dynamic world of business.
9. Financial Literacy

Financial Literacy Allows for Bigger Business Operations
A) The Importance of Financial Literacy in the Business World
Financial literacy is a crucial skill in the business world for various reasons, such as:
Informed Decision-Making:
Financial literacy empowers individuals to make informed and sound decisions related to:
- Investments
- Budgeting
- Financial planning
In the business world, decisions often have financial implications, and being financially literate helps in making choices that align with long-term goals and sustainability.
Risk Management:
Understanding financial concepts allows individuals to assess and manage risks effectively. In business, risk is inherent, and financial literacy helps in evaluating the financial risks associated with:
- Investments
- Projects
- Strategic decisions
This skill is crucial for developing risk mitigation strategies and ensuring financial stability.
Strategic Planning and Goal Setting:
Financial literacy plays a pivotal role in strategic planning and goal setting. Individuals with financial acumen can develop realistic and achievable financial goals for businesses. They can also create comprehensive financial plans that align with the overall business strategy, ensuring financial resources are allocated optimally.
Effective Communication:
Financial literacy facilitates effective communication within and outside the organization. Professionals who are well-versed in financial concepts can articulate financial information clearly to stakeholders, whether they are internal team members, investors, or external partners. Clear communication of financial data is essential for transparency and building trust.
Business Sustainability and Growth:
Financial literacy contributes to the sustainability and growth of a business. It enables individuals to:
- Manage cash flow efficiently
- Allocate resources wisely
- Identify opportunities for investment and expansion
Businesses with financially literate leadership are better equipped to adapt to changing market conditions and navigate economic challenges successfully.
In summary, financial literacy is a fundamental skill that enhances decision-making, risk management, strategic planning, communication, and overall business sustainability in the dynamic and complex world of business.
B) Tips for Developing and Improving Financial Literacy
Developing and improving financial literacy is an ongoing process. Here are five tips to enhance financial literacy in the business world:
Continuous Learning and Education:
Make sure you stay updated on:
- Financial trends
- Industry developments
- New financial tools
You should also be attending workshops, seminars, and online courses to expand your knowledge. Additionally, consider obtaining relevant certifications or degrees in finance to deepen your understanding of financial concepts and strategies.
Hands-On Experience:
Gain practical experience by actively managing finances, whether for a small project, a department, or even personal finances. This hands-on approach allows you to:
- Apply theoretical knowledge
- Learn from real-world scenarios
- Understand the consequences of financial decisions
Hands-on experience is one of the best ways to learn in the business world.
Network with Financial Experts:
Build a network with professionals who have expertise in finance! Do this by:
- Engaging in conversations
- Asking questions
- Seek mentorship
Learning from others’ experiences and insights can provide valuable perspectives and practical tips for navigating financial challenges.
Use Financial Tools and Technology:
Leverage financial tools and technologies to streamline financial processes and gain insights into data. Familiarize yourself with:
- Accounting software
- Budgeting apps
- Aata analytics tools
These tools can simplify complex financial information, making it more accessible and understandable.
Read Financial Literature:
Regularly read financial literature, including books, articles, and reports. This can help you stay informed about:
- Best practices
- Case studies
- Financial strategies
Choose materials that cater to your current skill level and gradually progress to more advanced topics as your understanding improves.
Remember that financial literacy is not developed overnight, and it requires a commitment to continuous improvement. By combining formal education, practical experience, networking, technology usage, and reading, you can significantly enhance your financial literacy in the business world.
C) Financial Literacy In Action
Financial literacy is a crucial skill for entrepreneurs and business leaders. It helps them understand their company’s financial health, make informed decisions, and gain the trust of potential investors. Below are some hypothetical examples of how financial literacy leads to business success:
Startup Founder:
An entrepreneur who creates a successful software company. This person is financially literate which allows them to understand financial statements, and track specific items that impact their company’s bottom line. This allows the company to keep growing strategically.
Retail Business Owner:
A successful retail business owner who has added multiple locations across a city. Their understanding of financial literacy helped them effectively manage cash flow, plan for expansion, while also navigating the struggles of scaling a business.
Social Impact Entrepreneur:
Their understanding of finance led them to secure funding from investors. This is because the entrepreneur was able to precisely communicate their financial strategies and demonstrate the sustainability of their business model.
All three of these examples are hypothetical, but they are used to demonstrate how being financially literate can help your business in more ways than one.
10. Technology Proficiency

Technology Proficiency Creates More Opportunities and Time
A) The Importance of Being Technologically Proficient in the Business World
In the modern business landscape, technological proficiency is no longer a luxury, but a necessity. Here are some key points that highlight its importance:
Efficiency and Productivity:
Technology can automate routine tasks, freeing up time for employees to focus on more complex and creative tasks. This can lead to increased productivity and efficiency. For example, customer relationship management (CRM) software can automate email marketing campaigns, allowing the marketing team to focus on strategy and content creation.
Data-Driven Decision-Making:
Technological tools can help businesses collect, analyze, and interpret data. This can lead to more informed and effective decision-making. For instance, analytics tools can provide insights into customer behaviour, market trends, and business performance.
Competitive Advantage:
Businesses that leverage technology effectively often have a competitive edge over those that do not. They can offer better products, services, or customer experiences. For example, e-commerce businesses that use AI for personalized recommendations can enhance the shopping experience and increase sales.
Innovation:
Technological proficiency can foster innovation. Businesses that are comfortable with technology are often better positioned to innovate and adapt to changing market conditions. For example, tech-savvy businesses can leverage emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain to create new products, improve operations, or disrupt traditional business models.
Remote Work:
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the ability to work remotely has become crucial. Technology makes remote work possible, allowing businesses to continue operating under challenging circumstances. For instance, video conferencing tools enable virtual meetings, collaboration software allows teams to work together in real time, and cloud-based tools ensure that employees can access necessary resources from anywhere.
To conclude, being technologically proficient is no longer a choice, it is necessary. There are endless ways that technology can help grow, build, expand, and improve your business while also saving you time, and more importantly, money. Being adaptable in today’s market is the difference between sinking and swimming.
B) Tips for Developing and Improving Technology Proficiency
In the business world, technological proficiency can be a game-changer. Here are some tips to develop and improve your technological proficiency:
Invest in Training:
Businesses should invest in training their employees on new technologies. This could involve in-house training programs, online courses, or workshops. The more technologically proficient the employees, the more competitive the business.
Leverage Data:
Businesses should leverage data to make informed decisions. This involves collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data. Tools like business intelligence (BI) software can help businesses gain insights from their data.
Implement Cybersecurity Measures:
With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, businesses must implement robust cybersecurity measures. This could involve using encryption, setting up firewalls, or conducting regular security audits.
Hire Tech-Savvy Staff:
When hiring new employees, businesses should look for individuals with tech skills. Tech-savvy employees can bring new ideas, improve processes, and help the business stay competitive.
Automate Where Possible:
Automation can save businesses time and money. This could involve automating repetitive tasks, using AI for customer service, or implementing robotic process automation (RPA).
Remember, technological proficiency is not just about using the latest tools. It’s about understanding how technology can enhance various aspects of a business, from productivity and decision-making to competitiveness and innovation. It’s about being adaptable and ready to leverage technology to meet the changing needs of the market and the business environment.
C) Technology Proficiency In Action
Technology proficiency in action can be leveraged in many ways that consumers aren’t aware of, here are three examples of technology proficiency in action:
E-commerce Business:
An e-commerce business uses data analytics tools to understand customer behaviour and preferences. They analyze data from their website and social media platforms to identify trends and patterns. This information is used to personalize the shopping experience for their customers, recommend products, and tailor marketing campaigns. This leads to increased customer satisfaction and sales.
Manufacturing Company:
A manufacturing company implements IoT (Internet of Things) technology in their production line. Sensors are installed on machines to monitor performance and detect issues in real time. This allows the company to perform predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency. The company also uses AI (Artificial Intelligence) to optimize their supply chain, predicting demand and managing inventory more effectively.
Healthcare Provider:
A healthcare provider leverages telemedicine technology to provide remote care to patients. They use video conferencing tools for virtual consultations, electronic health records to store and access patient information, and mobile apps for appointment scheduling and medication reminders. This improves access to healthcare services, particularly for patients in remote areas, and enhances patient engagement and satisfaction.
These examples illustrate how businesses can leverage technology to improve their operations, provide better services, and gain a competitive edge. Technological proficiency enables businesses to make the most of these opportunities.

