Effective communication is critical for every business, but phone system issues can disrupt operations and frustrate employees and customers alike. In this business phone troubleshooting guide, we cover everything from physical cable problems and desk phone malfunctions to VoIP, Wi-Fi, and video call issues. Whether you’re dealing with static, dropped calls, or connectivity problems, this guide provides actionable solutions and best practices to keep your business phones running smoothly.
- Troubleshooting Physical Connections
- Troubleshooting Business Phones
- Troubleshooting VoIP & Network-Dependent Phones
- Troubleshooting Wi-Fi or Wireless Phones
- Troubleshooting Call Quality
- Troubleshooting Video & Unified Communications
- Troubleshooting Network Infrastructure
- Preventive Maintenance & Best Practices
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Interactive Decision Tree for Business Phone Troubleshooting
- When to Call a Professional
Follow this guide step by step to quickly identify and resolve business phone issues, or contact Network Telecom for expert support when you need professional assistance.
Key Takeaways
- Check Physical Connections: Regularly checking physical connections, such as cables, jacks, and handsets, can prevent most common phone issues.
- Address Phone Power & Configuration: Power, configuration, and manufacturer-specific problems should be addressed carefully to maintain reliable operation of individual business phones.
- Optimize Network & VoIP Settings: Network-dependent phones and VoIP systems require stable internet connections, proper firewall and QoS settings, and correct SIP registration for optimal performance.
- Maintain Wireless Signal Strength: Wireless phones need strong Wi-Fi signals, minimal interference, and proper roaming setup to function effectively in larger offices.
- Resolve Call Quality Issues: Call quality issues are often caused by bandwidth limitations, echo, latency, or improper codec selection and can usually be resolved by optimizing network and device settings.
- Ensure Video & Unified Communication Reliability: Video calls and unified communications platforms require sufficient system resources, updated software, and correctly configured peripherals to maintain clear audio and video.
- Follow Preventive Maintenance: Preventive maintenance, including software updates, network documentation, and staff training, helps minimize disruptions and ensures a reliable business phone system.
- Know When to Call a Professional: Knowing when to call a certified telecom or IT professional is critical for complex tasks such as major network rewiring, SIP trunk setup, and advanced VoIP QoS configuration.
- Rely on Expert Support: Network Telecom provides expert support to resolve advanced phone system issues, optimize performance, and keep your business communications running smoothly.
Business Phone Troubleshooting
1. Troubleshooting Physical Connections
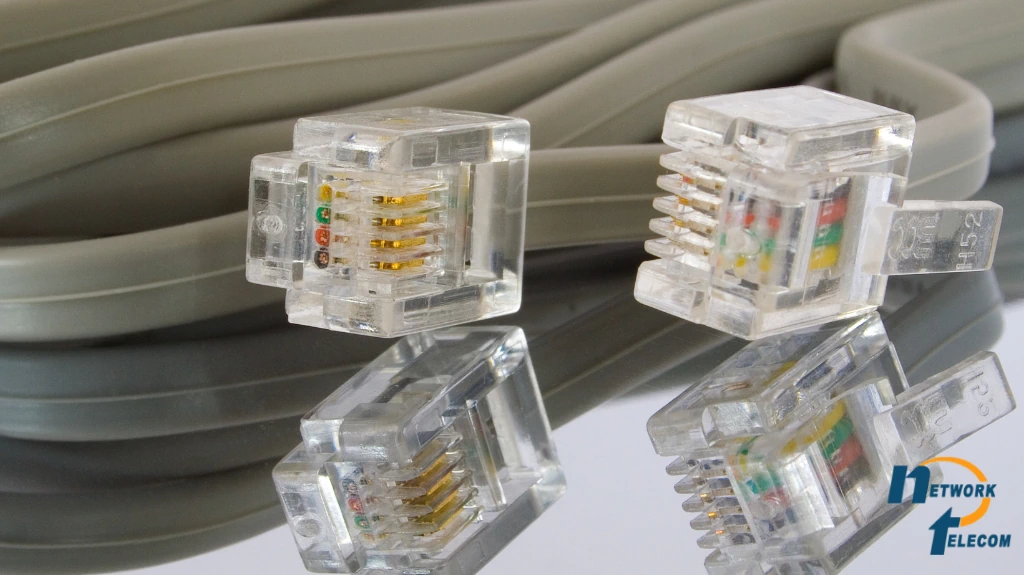

In troubleshooting complicated phone system configuration or network installations, a good starting point is to start with the basics: the physical connections. Loose, defective cables, broken jacks, or electromagnetic interference from nearby devices are the most frequent causes of poor call quality, static, or dropped calls. By thoroughly inspecting your cables and connections, most issues will be resolved easily without needing technical expertise.
Common Issues with Phone Cables and Jacks
Start by inspecting the cables and jacks that link your phones. Over time, cables can become worn, frayed, or loose, producing buzzing, crackling, or dropped calls. Minimal wear and tear can result in occasional issues that appear random but are easy to fix.
Phone Line Cable Checking Tips:
- Inspect each cable for visible damage such as cuts, kinks, or bent connectors.
- Make sure each cable is correctly plugged into the correct jack; loose connections are surprisingly common culprits for problems.
- If you see discoloration or corrosion on connectors, swap out the cable immediately to prevent call quality issues.
- Once you’ve checked over your cables, it’s helpful to be aware of the different types of connections you’ll encounter.
Learning about RJ11, RJ45, and Ethernet Connections
Phones in a corporate setting can have different types of connectors, each for a specific purpose:
- RJ11: RJ11 is the standard telephone plug used for old-style analog (landline) phones. These usually feature smaller connectors with 4 or 6 wires.
- RJ45 / Ethernet: The RJ45 is the plug that you insert your Ethernet cable into. This type of plug is used for VoIP phones and network connections. These are a bit larger connectors with 8 wires and are even used sometimes by your office network.
How to Test and Test These Connections:
- Make sure all the cables are seated correctly in their jack. Press down gently until you hear a click.
- Swap the cable for a known working one to determine if the problem persists.
- Use a simple line tester or multimeter if you have one available; such tools can pick up breaks or shorts in the wiring.
Dealing with Crackling or Buzzing Lines
If your calls are buzzing, cracking, or breaking up and going in and out, the problem may be with your line rather than with the phone itself. Previous Network Telecom manuals provide detailed guidance on how to diagnose such problems, including interference, grounding, or damaged lines. You can check these guides out here:
- How to Fix Poor Telephone Line Call Quality: Crackling, Buzzing Noise or Cutting In and Out
- Small Business Phone Systems Top Problem & Fixes
Potential Sources of Interference:
The following are some possible sources of interference with your call quality:
- Other electrical devices in close proximity, such as printers, microwaves, or fluorescent lighting.
- Wireless devices such as routers, cordless telephones, or security systems.
- Power spikes or faulty grounding on your office cabling.
Tools and Tips for Physical Troubleshooting
Equipped with the proper tools, it can be much simpler to diagnose and repair connection problems.
Recommended Tools:
- Multimeter: A multimeter is a handy tool for continuity and voltage testing in cables.
- Line tester: Basic line testers will locate faults on phone lines and pin down dead spots.
- Replacement cables and connectors: It is a good idea to keep several spare RJ11 or Ethernet cables available for quick replacement.
By performing these fundamental checks and using the appropriate equipment, you can resolve many typical phone issues prior to the issue affecting your business operations. Physical connection problems are usually the easiest to resolve, and it makes sense to address them first to save time and aggravation.
2. Troubleshooting Business Phones

Once you’ve confirmed that your office’s physical connections are functioning properly, the next step is to focus on the phones themselves. Desk phones, cordless phones, and VoIP phones can malfunction despite the network or wiring. By going through the power, setup, and standard manufacturer’s issues one by one, you can often resolve the issue without needing a technician.
Power Issues: Phones Not Turning On or Display Issues
Many phone problems are power-related. If the phone fails to turn on, the screen is blank, or the lights flash randomly, it may be a power problem and not a problem with the device itself.
Power Issue Diagnosis Tips:
- Ensure that the power cable is securely connected to the phone and the outlet or the PoE (Power over Ethernet) switch.
- If a PoE-capable phone is being used, verify that the network switch port is working properly.
- Inspect the power adapter and cable for any outward visible damage. Replace if damaged.
- For cordless phones, ensure the batteries are installed correctly and charged.
- In case the phone will not power up, attempt using a different power supply or cable to eliminate a defective adapter.
By ensuring that the unit is receiving a stable power, you can eliminate one of the most common phone problems.
Configuration and Reset: Restore to Default Settings
Occasionally, the phone settings or programming may be making the unit behave erratically. A reset or a reprograming of the extension will usually fix these issues.
Steps in Configuration and Reset:
- Refer to the user manual contained in the manufacturer’s kit to reset the phone to factory settings. This will delete any misconfigurations and return the phone to its original settings.
- Carefully reconfigure the line or extension settings to suit your office’s internal number and configuration system.
- Document changes to facilitate restoration when needed.
- Test the phone after a reset by making a call to verify its working condition.
A properly configured phone ensures smooth operation and reduces ongoing troubleshooting needs.
Common Manufacturer Issues
There are phone models that have ongoing issues or unique troubleshooting processes. Familiarity with them may reduce the time needed.
Avaya Phones:
Avaya desk phones may sometimes present registration issues or fail to register at the server. Read the Avaya phone’s troubleshooting and support manual for step-by-step fixes.
Poly, Cisco, and Yealink Phones:
- Poly phones suffer from call quality issues if the firmware is not up to date.
- Cisco phones sometimes require reboots after network changes.
- Yealink phones suffer from SIP registration failure, which is resolved by validating extension credentials and network settings.
Having knowledge of the usual manufacturer-specific issues ensures quicker identification and fixing of phone issues.
Battery and Handset Tests for Cordless Phones
Cordless phones introduce some additional potential issues to those of wired desktop phones. Batteries, charger bases, and handset placement can all affect performance.
Battery and Handset Reminders:
- Check that batteries are correctly installed and charged.
- Ensure handsets are seated properly within their charger bases.
- Change old batteries that won’t charge anymore.
- Test the handset in another charger base to rule out a faulty charger.
Regular cordless handset inspections prevent unexpected loss of calls and improve overall reliability.
Applying these protocols: power checking, configuration verification, familiarity with manufacturer quirks, and fresh batteries, you can diagnose the most common business telephone issues without technical expertise. Being proactive in this way keeps your office communication up and running and reduces downtime.
3. Troubleshooting VoIP & Network-Dependent Phones
For businesses using VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) phones or IP-based desktop phones, issues often extend beyond the handset itself. These phones rely on a stable network connection, proper configuration, and sufficient bandwidth to function correctly. By confirming network connections and elementary settings, the majority of issues can be resolved without requiring extensive technical knowledge.
Checking Network Connectivity
VoIP phones need a functioning network to receive and make calls. Any temporary network disruption will cause dropped calls, delayed audio, or failure to register with the phone system.
Network Connectivity Checking Tips:
- Ensure that the Ethernet cable is securely connected to both the phone and the network.
- Verify that other devices on the same network, such as computers, are accessing the internet.
- Restart the network switch or router if multiple devices are experiencing connectivity issues.
- For phones connected via Wi-Fi, make sure the signal is strong and the phone is connected to the correct SSID (Service Set Identifier).
Checking basic connectivity can immediately resolve a vast majority of call quality and registration problems.
Firewall and Port Considerations
VoIP phones utilize specific network ports to communicate. Your phone may not register or experience call issues if these ports are blocked by a firewall.
Steps to Confirm Firewall and Port Settings:
- Ensure that SIP and RTP traffic (two popular VoIP protocols) are allowed by your network firewall.
- Ensure that the phone’s IP address is not blocked by your router or firewall.
- Confirm with your VoIP service provider the specific ports your system requires.
Keeping the necessary ports open allows the phone to communicate properly with the VoIP server.
Quality of Service (QoS) Settings
In networks with a lot of traffic, voice traffic can be disrupted by other high-bandwidth activities like large file downloads or video playback. Quality of Service (QoS) settings give priority to telephone traffic for clear audio.
QoS Tips for Non-Technical Users:
- Check that your office router is QoS-capable. Most newer routers include simple QoS configuration settings.
- Assign a higher priority to your VoIP phones’ IP addresses or MAC addresses.
- Simple prioritization will prevent dropped calls and choppy voice quality.
Prioritizing phone traffic will ensure voice calls are clear even when other devices are using the network.
SIP Errors and Troubleshooting
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) errors will appear in the form of messages like “Registration Failed” or “SIP Timeout.” SIP errors typically indicate a problem with communication between your phone and the VoIP server.
Troubleshooting Steps to Fix SIP Issues:
- Verify that the phone extension, username, and password are correctly configured.
- Reboot the phone to re-register with the server.
- Verify network connectivity, as SIP errors will most likely appear when a phone cannot connect to the server.
The majority of SIP errors are simple to fix by checking settings and network connectivity.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) Issues
Some VoIP phones are powered directly from the Ethernet cable using PoE. If the phone will not power on, it could be a PoE issue.
PoE Troubleshooting Tips:
- Check that the Ethernet cable is plugged into a PoE-enabled port.
- Test the phone on a known good working PoE port to rule out switch issues.
- If necessary, use an external power adapter as a temporary troubleshooting solution for PoE problems.
Verifying PoE connections ensures your phones remain powered and functional without unjustified downtime.
By performing these actions: verifying connectivity, ensuring firewall and QoS configurations are appropriate, resolving SIP errors, and checking PoE functionality, you can troubleshoot most network-dependent phone problems without the need for specialized technical expertise. This maintains your office communication seamless and reliable.
4. Troubleshooting Wi-Fi or Wireless Phones
Wireless phones like DECT (Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications) phones and softphones via Wi-Fi are a blessing in offices but can pose special problems. Lost calls, bad audio, or no connection are typically due to interference in signals, improper settings, or network congestion. Knowing these common problems in advance, you can get wireless phones up and running like a charm.
Checking Signal Strength and Coverage
Weak Wi-Fi signal is among the most common causes of call dropping or poor voice quality on wireless handsets.
Strong Signal Tips:
- Keep the phone base or handset nearer to a Wi-Fi access point if possible.
- Avoid placing devices near large metal objects or electronic devices that may dampen or jam the signal.
- Ensure your office Wi-Fi network reaches everywhere where phones are intended to be used. Install additional access points, if required.
Excellent and consistent Wi-Fi coverage is essential to provide clear, uninterrupted calls.
Verifying Network Credentials
Incorrect network credentials may render a wireless phone unable to register with your office network.
Steps to Validate Credentials:
- Make sure the handset is well connected to the intended Wi-Fi network (SSID).
- Double-check the Wi-Fi password; even small typos can prevent connection.
- Ensure that the phone’s IP settings are correct if your network uses static IP addresses.
Correct credentials allow the phone to communicate reliably with your VoIP server and other network devices.
Avoiding Channel Conflicts and Interference
Multiple devices on the same Wi-Fi channel can interfere with phone calls, resulting in audio issues or dropped connections.
Interference Solutions:
- Use your router or access point’s admin page to verify current Wi-Fi channels.
- Change to a less busy channel if available. Most new routers can automatically choose the best channel.
- Reduce interference from other devices like cordless phones, microwave ovens, or Bluetooth devices close to the handset.
Lower interference provides more stable connections and better-sounding calls.
Solving Roaming Problems
In larger offices that have more than one access point, wireless phones drop calls while roaming from one coverage area to another.
Optimizing Roaming Tips:
- Put all access points on the same network and properly set up for seamless handoff.
- Walk test the phone across different areas to identify dead spots or zones of lack of coverage.
- Upgrade access points or add repeaters if persistent, recurring problems occur.
Proper Wi-Fi setup and thoughtful placement of access points allow cordless and softphones to function reliably throughout your office.
With proper monitoring of signal quality, credentials, interference, and roaming behavior, most wireless phone issues can be resolved at once and with no technical assistance. Your employees are able to communicate freely and effectively wherever they happen to be in the office.
5. Troubleshooting Call Quality
Even if phones are powered, connected, and configured correctly, you may still experience poor call quality. Issues such as static, crackling, delayed audio, or dropped calls may disrupt communication and impact productivity. Troubleshooting call quality involves identifying the source of the issue and taking action to resolve it.
Identifying the Source of Poor Call Quality
Call quality problems can be due to the service provider, network, or phone.
Steps to Identify the Cause:
- Use other phones on the same line to see if the issue is on all phones or just one.
- Make a call from a different location or network to see if the problem exists in a specific area.
- Swap cables or power adapters to rule out simple hardware issues.
Identifying the cause focuses the problem and ensures that you address the right problem.
Optimizing Codecs
VoIP phones use audio codecs to compress and transmit voice data. Choosing the appropriate codec can significantly impact call quality.
Codec Tips:
- Use codecs recommended by your VoIP provider for your specific network conditions.
- Avoid using very compressed codecs under networks with unstable conditions.
- Experiment with different codecs if calls consistently have bad audio.
Codec optimization ensures that voice signals are transmitted clearly with minimal loss of data.
Troubleshooting Echo and Latency Issues
Echo or delayed sound can make calls unusable and frustrating.
Tips for Reducing Echo and Latency:
- Ensure your network provides sufficient bandwidth to handle all simultaneous calls and internet activity.
- Avoid using high-bandwidth applications during important calls.
- Adjust phone or headset microphone and speaker settings to minimize feedback.
Repairing latency and echo will make your calls clearer and less irritating to conduct.
Managing Bandwidth and Network Congestion
Insufficient network bandwidth results in cutting in and out of audio, especially in offices with multiple VoIP phones.
Network Optimization Tips:
- Prioritize voice traffic using Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your router.
- Restrict non-essential network utilization when there are ongoing calls during peak hours.
- Verify with your ISP (Internet Service Provider) that your internet package supports enough upload and download speed for your call volume.
Adequate bandwidth ensures smoother, unbroken calls for everyone in the office.
Debugging Microsoft Teams and Other VoIP Software
Most businesses use Microsoft Teams, Zoom, or other collaborative software to make calls. Call quality issues within these applications typically relate to network settings or device compatibility.
Practical Solutions:
- Ensure that your device has the current app versions.
- Close apps that are unnecessary and may be utilizing bandwidth or CPU resources.
- Attempt calls using a wired connection if Wi-Fi issues persist.
Consult platform-specific troubleshooting guides for Teams or Zoom for more advanced issues.
By systematically identifying the root cause of call quality issues, optimizing network settings, and adjusting device settings, most issues can be resolved without the need for technical expertise. Solid, clear calls keep your productivity and customer satisfaction intact.
6. Troubleshooting Video & Unified Communications

Video calls and unified communications platforms are essential tools for modern businesses. However, video freezes, audio delays, or poor synchronization between audio and video can disrupt meetings and reduce productivity. Many of these issues can be resolved with straightforward troubleshooting steps, even if you’re not a technical expert.
Resolving Video Call Freezes or Lag
Frozen video playback is most often caused by low bandwidth, network saturation, or a faulty device.
Optimizing Video Performance:
- Ensure that your computer or device meets the minimum system specifications set for the video platform.
- Uninstall unused programs that are hogging processing power or internet bandwidth.
- Use a wired Ethernet link where available to build a more stable network than Wi-Fi.
- Reduce the video resolution from settings if there is a slow and unstable internet connection.
Following these steps guarantees smooth video communication and less disturbance during calls.
Fixing Audio and Video Sync Problems
Out-of-sync audio and video can be annoying and disorienting to participants.
Workarounds for Sync Problems:
- Restart the video application and device to fix transient problems.
- Check that your device’s audio and video drivers are up to date.
- Ensure no other applications are using high network bandwidth while on call.
- Test with a different headset or camera to rule out hardware issues.
Proper synchronization of audio and video ensures the meetings are sharp and professional.
Attending Meetings: Microsoft Teams, Zoom, and Other Options
Sometimes call issues arise even before the meeting begins due to login errors or platform configurations.
Tips for Effortless Meeting Access:
- Verify your login credentials and access to the platform.
- Ensure the application is updated to the latest version.
- Test your speakers, microphone, and camera before joining the meeting.
- Utilize platform-specific tutorials for common issues, i.e., how to join a Microsoft Teams meeting.
Advanced setting checks prevent latencies and technical issues during meetings.
Peripherals: Speakers, Webcams, and Headsets
Peripheral peripherals such as headsets and webcams influence video calling quality.
Peripheral Troubleshooting:
- Make sure the device is appropriately connected and detected by your smartphone or computer.
- Update driver software or firmware when it is available.
- Try out the device on another computer or application to ensure it’s working properly.
- Use a wired connection for headsets and cameras wherever possible to reduce interference.
Making peripherals work appropriately allows your video calls to run smoothly and professionally.
By testing bandwidth periodically, equipment setups, software versions, and peripherals, most video and unified communications issues will correct themselves easily. Good-quality video calling improves teamwork and keeps your employees connected, even when they are telecommuting.
7. Troubleshooting Network Infrastructure
A solid and properly set-up network is the backbone of any business telephone system. Network issues can affect both voice and video calls, resulting in dropped calls, garbled sound, or failure to connect. Fixing common network issues and making sure your infrastructure is sound is something you can do in order to ensure your phones function properly.
Checking Routers and Modems
Routers and modems manage data transit through your network, and issues there can influence your phone directly.
Router and Modem Check Tips:
- Restart the router and modem to flush out network connections.
- Ensure firmware is up to date; manufacturers issue updates to stabilize systems and make them more secure.
- Ensure devices are properly plugged into power and network jacks.
- Verify for excessive heat, which can cause erratic network challenges.
Basic router and modem troubleshooting can repair most connection issues.
Switch Port Issues
A switch port is a hardware device that allows computers to communicate with each other. It uses packet switching to receive and forward data between devices on your network. There are a number of phones and computers that are linked via network switches in bigger offices. A mistake in a switch port can leave one or more phones out of the connection.
Fixing Switch Ports:
- Plug the phone into another switch port to prevent a bad connection.
- Clean ports for dust, breakage, or loose wires.
- Label ports and cables to keep track of which devices are connected where, making troubleshooting easier in the future.
Switch port checks help pinpoint specific hardware issues without affecting the entire network.
IP Conflicts and DHCP Problems
Every device on a network needs a unique IP address. Conflicts or misconfigurations can prevent phones from registering or connecting properly.
Tips for Resolving IP Issues:
- Reboot the problem phone to allow it to request a new IP address from the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server.
- Verify that static IPs do not conflict with other devices in the network.
- Verify with your network administrator whether multiple devices are experiencing IP conflicts.
Efficient IP management ensures devices communicate reliably without interference.
VLAN and QoS Configuration
For multi-department or heavily used networks, QoS settings and VLANs (Virtual LANs) are employed to prioritize voice traffic and segregate it from the rest of the data.
Network Configuration Tips:
- Ensure that phones are assigned to the correct VLAN if your network is divided.
- Double-check that QoS is configured to prioritize voice and video traffic above lower-priority data.
- If unsure, consult with a network expert to configure it properly.
Correct VLAN and QoS settings prevent voice traffic from being interrupted by excessive usage of the network.
ISP Disruptions and External Issues
The problem might be outside your office network at times. ISP (Internet Service Provider) outages or disruptions can affect VoIP calls and internet access.
Testing for External Issues:
- Contact your ISP to know if there are any known service disruptions.
- Use online tests to verify internet speed and latency.
- Schedule backup options such as cellular failover or secondary connections in case phone continuity is vital.
By proactively checking internal and external network health, you can minimize disruptions and have a reliable business phone system.
8. Preventive Maintenance & Best Practices
Preventive maintenance is the foremost strategy to minimize business phone issues before disrupting communication. By simple, regular checks and best practices, office administrators and administrative staff can help maintain phones, networks, and peripherals in working order.
Regular Physical Checks
Physical checks regularly on hardware and connections help to locate minor problems before they escalate to become major issues.
Physical Maintenance Tips:
- Check cables, jacks, and connectors monthly for wear, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Inspect handsets and phones for external damage, and functioning of buttons and screens.
- Verify cordless phones’ charging and schedule battery replacements as needed.
Routine physical checks prevent minute issues from building up to full-fledged interruptions.
Software and Firmware Updates
Phone, router, switch, and peripherals all require periodic updates to run at their best.
Update Recommendations:
- Institute routine updates for phone firmware and VoIP software.
- Update network equipment and routers with the most recent firmware versions.
- Ensure drivers for webcams, headsets, and other peripherals are current.
Keeping software and firmware current reduces bugs, improves security, and optimizes compatibility.
Network Monitoring and Documentation
Having your network setup documented and monitoring performance can hasten and simplify troubleshooting.
Best Practices for Monitoring:
- Keep a rough diagram of your phone and network connections.
- Keep phone extension lists, IP addresses, and device locations.
- Manage call quality, network uptime, and bandwidth with monitoring software.
Good documentation guarantees that anyone who must debug issues can instantly recognize potential areas for trouble.
Training and Staff Awareness
Educating staff on proper use of the phone and basic troubleshooting can ensure removal of common problems.
Staff training tips:
- Train staff to plug and unplug equipment correctly without ruining connectors.
- Incentivize reporting sporadic problems immediately and not waiting for them to accumulate.
- Offer simple rebooting procedures for phones or checking connections before visiting IT support.
Empowering staff aids in resolving small problems without assistance, reducing downtime for the entire office.
By performing regular maintenance, keeping devices up to date, keeping your network on a catalog, and training employees, companies can prevent most typical issues within their phone systems. Being proactive saves time, avoids frustration, and keeps your employees connected reliably.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Repairing business phones may appear overwhelming, especially if you are not a technical genius. Below are answers to commonly asked questions that administrative assistants, office managers, and small business operators usually ask regarding phone systems.
10. Interactive Decision Tree for Business Phone Troubleshooting
Phone issues can be frustrating, but not every problem requires a service call. To help you quickly identify and resolve common issues, we’ve created this interactive decision tree. Simply follow the steps based on the problem you’re experiencing; whether it’s a phone that won’t turn on, static during calls, dropped VoIP connections, or video conferencing glitches.
At each step, you’ll see suggested troubleshooting actions, and if the issue persists, you’ll know exactly when it’s time to reach out to Network Telecom for expert support.
• Phone won’t turn on
• Call quality issues
• Wireless/VoIP call drops
• Video/Unified communications
Check power cable & connections → Is display on?
Are other phones affected?
Check Wi-Fi signal → Strong?
Check bandwidth & close unnecessary apps → Test call → Use wired connection → Adjust video resolution → Still freezing? → Contact Network Telecom
10. When to Call a Professional

While the majority of business telephone issues can be addressed with quick troubleshooting, others are outside amateur capabilities and require the hand of a certified telecom or IT professional. Being able to recognize when to call a professional guarantees issues are solved safely and without interruption, preventing downtime and your office communications systems.
Issues That Require a Professional
Some problems are more involved than do-it-yourself fixes and require professionals to fix them:
- Massive Network Rewiring: During your office refurbishment, moving offices, or adding lots of new devices, expert guidance verifies proper cabling, port configuration, and conformity to standards.
- SIP Trunk Configuration: SIP trunk installation or reinstallation for VoIP requires meticulous configuration to ensure hassle-free call forwarding, proper assignment of bandwidth, and secure connection.
- Advanced VoIP QoS Configuration: Prioritize voice traffic through complex networks by at times installing routers, switches, and firewalls. A professional configures settings in order to maintain active calls running without interruptions and avoid tampering with other traffic.
Recognizing such circumstances in advance prevents misconfigurations that can disturb your whole telephone system.
Call Network Telecom for Professional Assistance
Network Telecom provides qualified telecom and IT professionals that can handle advanced configuration, troubleshooting, and maintenance. Whether it’s a small office refresh or a large enterprise VoIP installation, our team keeps your phone system working.
Contact us today for expert assistance:
Phone: 519-748-2226 x600
Email:
Website Contact Form: https://network-telecom.com/contact
By knowing when to call in the experts, you safeguard your business from lengthy downtime, provide secure communication, and have peace of mind in the knowledge that your phone system is in competent care.
Optional Additions
“The entire project was orchestrated with minimal telephone system downtime, and the ongoing support we have received from them has been reliable and efficient.”

